CyCTF 2025 Quals - Mobile Writeups
Hello everyone, In this writeup, I will show you how I solved Grand Theft Mobile and Vault Raider mobile challenges from CyCTF, powered by CyShield. Let’s get started.
Grand Theft Mobile

Let’s download the APK file and start the app on an android emulator to see how it works at runtime.
We can see that it provides us with a user-input to enter name and a button to submit.
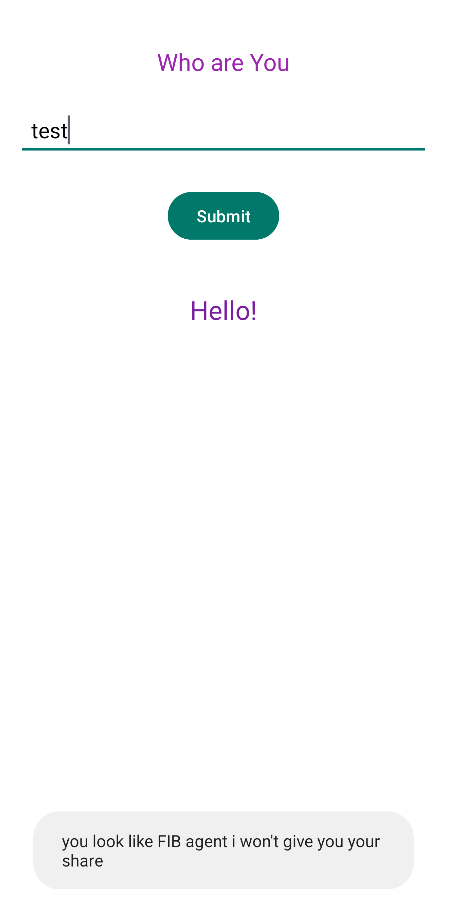
If we enter a random name, it shows us the following message: you look like FIP agent i won't give you your share.
Nothing else, so let’s start analyzing the source code using JADX-GUI.
AndroidManifest.xml Analysis

- Uses the SDK version
34and the minimum version is25. - Declares
DYNAMIC_RECEIVER_NOT_EXPORTED_PERMISSIONthat Android automatically adds to applications targeting API level 33 (Android 13) or higher. Its purpose is to enhance security by preventing other applications from connecting to dynamic broadcast receivers without explicit permission. - Defines an
MainAcvitiyand export it totrue. - Adds
intent-filtertoMainAcvitiyto beLAUNCHERwithandroid.intent.action.MAIN(which means the first screen appears when you open the app as we see above). androidx.startup.InitializationProvideris a part ofAndroidXApp Startup library. It’s aContentProviderused to initialize libraries at app start.android:exported="false"— not available to other apps.android:authorities— unique authority string required for provider identification.<meta-data>entries tell the startup provider which initializers to run (EmojiCompat, Lifecycle, Profile Installer, etc.). These are normal library bootstrapping entries.- Declares a
BroadcastReceiverfrom AndroidX Profile Installer library. android:permission="android.permission.DUMP"is to tell senders must hold theDUMPpermission to send broadcasts to this receiver.DUMPis a privileged/system-level permission (normally restricted), so typical third-party apps cannot send those broadcasts.android:enabled="true"the receiver is active.android:exported="true"the receiver can receive broadcasts from other apps (subject to permission). Combined withDUMPrequirement usually prevents unprivileged apps from reaching it.android:directBootAware="false"makes the component not run before device unlock, and it also prevents the component from accessing device-protected storage before the user has unlocked the device. This- The
intent-filterentries list the actions this receiver listens for (install/save profiles, benchmark ops).
Let’s navigate to ManActivity.
MainActivity.java Analysis
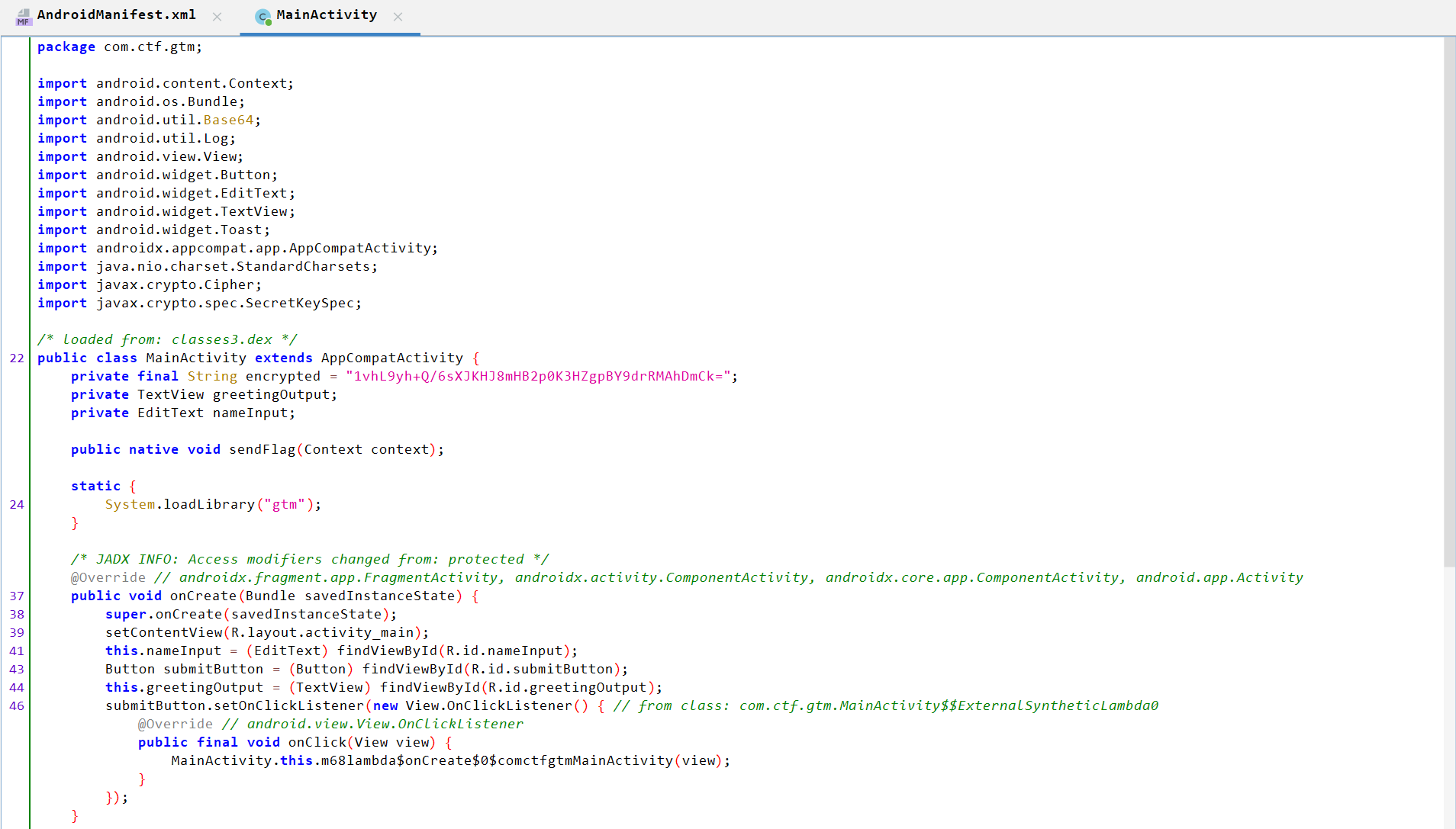
- Declares
encryptedstring with a value:1vhL9yh+Q/6sXJKHJ8mHB2p0K3HZgpBY9drRMAhDmCk=. - Declares
TextView greetingOutputandEditText nameInputand handle them ononCreate()function (related to UI). - Declares a native (JNI) method
sendFlag(Context)implemented in a native librarylibgtm.so. System.loadLibrary("gtm")loads that library at class load time.m68lambda$onCreate$0$comctfgtmMainActivityAnalysis:- Writes a log message to the Android system log (logcat).
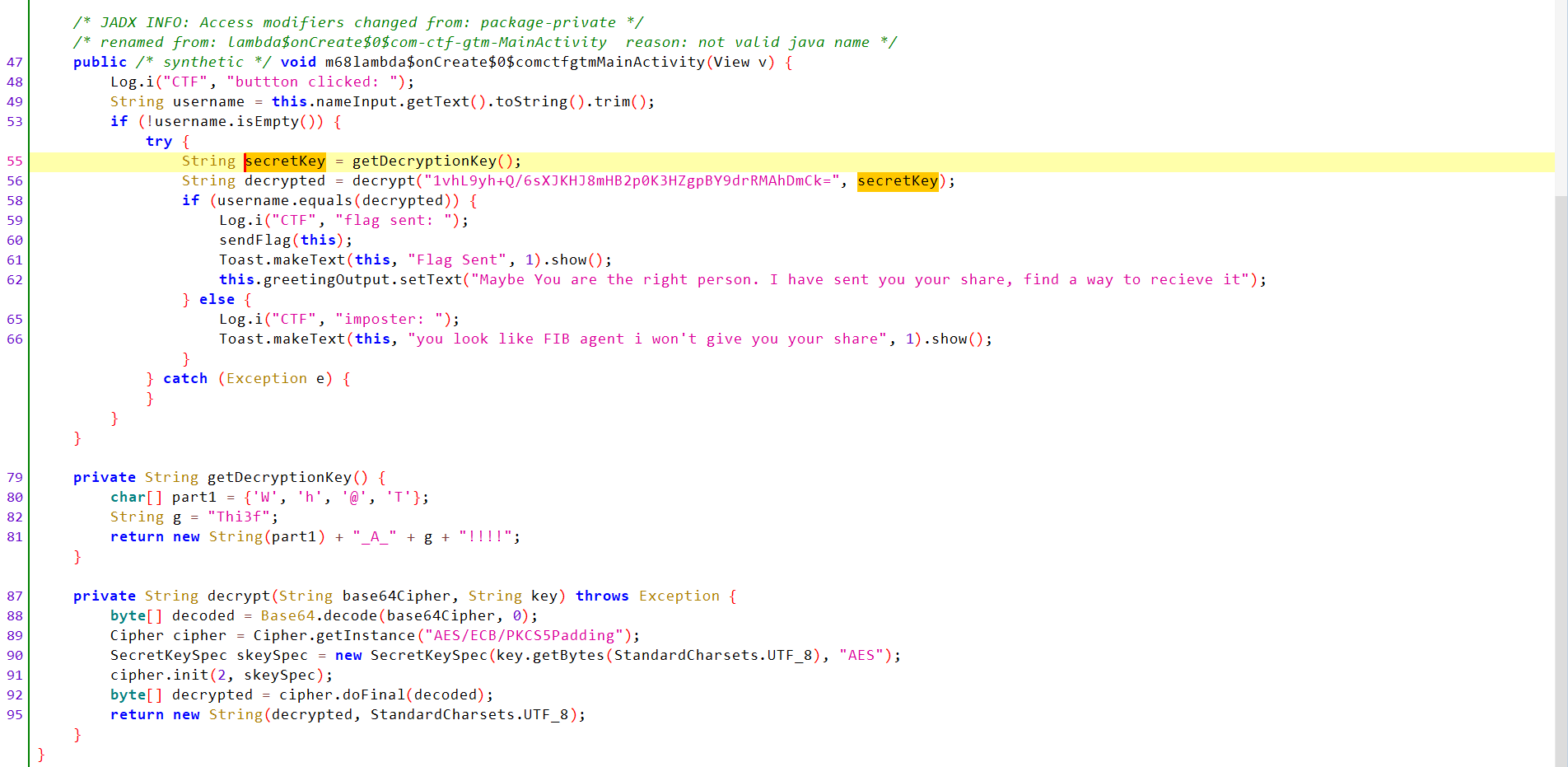
- Declares
usernamestring and assign the user-input value to it. - If the
usernameis not empty:- Declares a
secretKeystring and assign the returned value fromgetDecryptionKey()function to it. - Declares ` decrypted
string and assign the returned value fromdecrypt()` function to it. - If username equals decrypted, it writes a log message (
flag sent:) and calls nativesendFlag(this)
- Declares a
- If not match, it shows an “imposter” toast.
getDecryptionKeyAnalysis:- Declares an array of characters.
- Declares a
gstring with value:Thi3f. - Returns the the combination of some strings to be:
wh@T_A_Thi3f!!!!(which is the secret).
decryptAnalysis:- Base64-decodes the input ciphertext.
- Uses AES in ECB mode with PKCS#5/7 padding.
- Initializes cipher for decrypt (
cipher.init(2, skeySpec)—2isCipher.DECRYPT_MODE). - Decrypts and returns the plaintext string.
We need to submit a username which equals to decrypted value from decrypt() function to get the flag.
We have the encrypted value and the secret, so we can decrypt it using the following script:
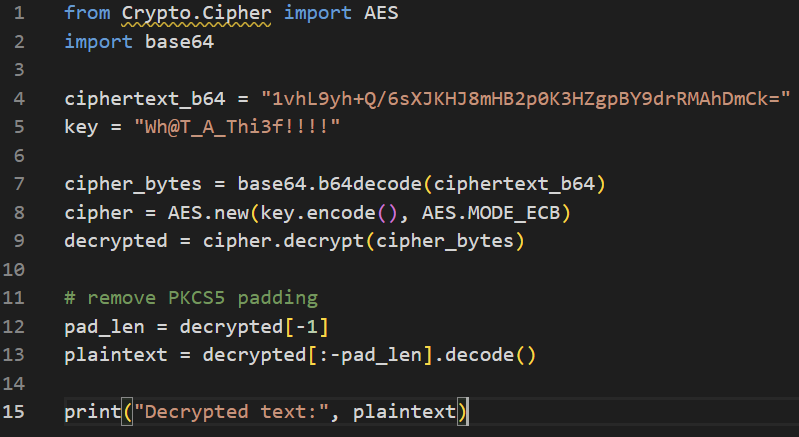

Now, if we submit the username as Tr3V0R_not_Micheal, we can see the flag sent message but the flag itself not appeared in logs or in UI. That means the flag is transferred internally.
So, what we can do is to dump the memory and check whether the flag is retrieved there.
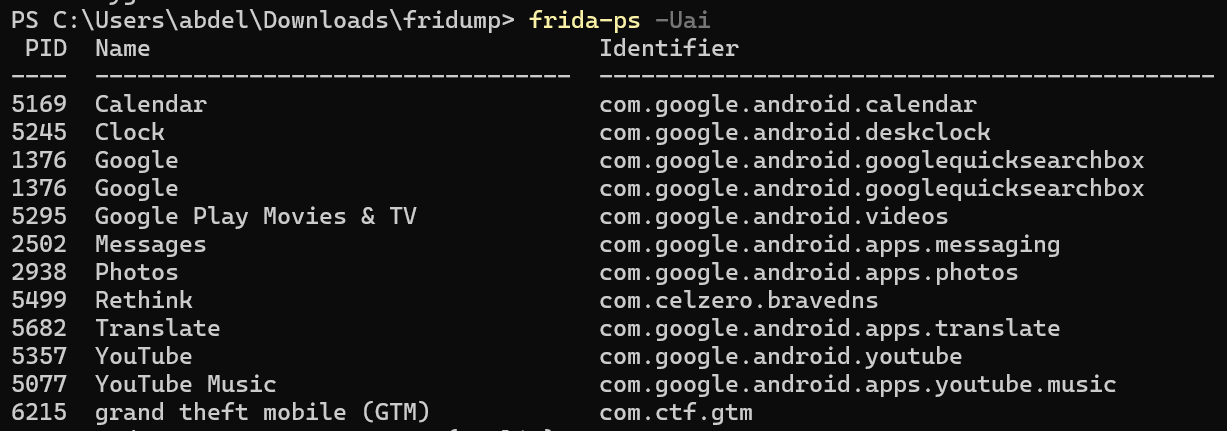
Let’s get the process id (PID) of the the app then run fridump to dump the memory.
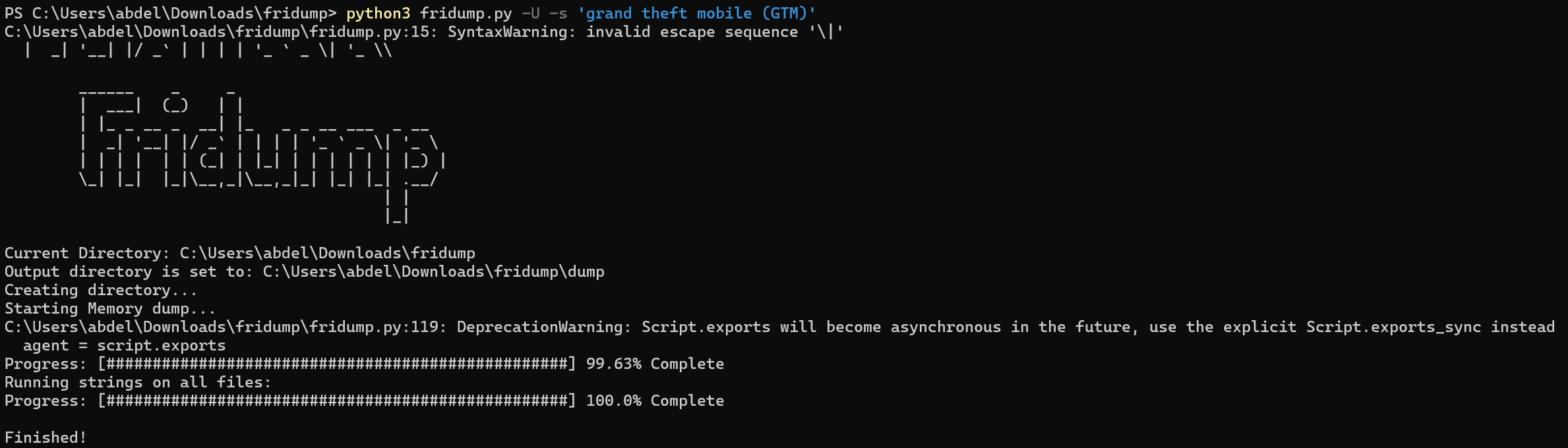
If we read the strings.txt file, we can find the flag.

Flag: cyctf{aX9tG4LkZp72MvBQeC3AH8OGMJ}
Vault Raider
Like the previous challenge, let’s the run the APK on an android emulator to examine it at runtime.
We can see that it shows us a blank screen with text in the center and the bottom there is a toast which tells us Incorrect Master Key!

Let’s analyze the source code.
The android manifest is like the previous one with one activity (MainActivity), so without wasting time, let’s move to MainActivity.
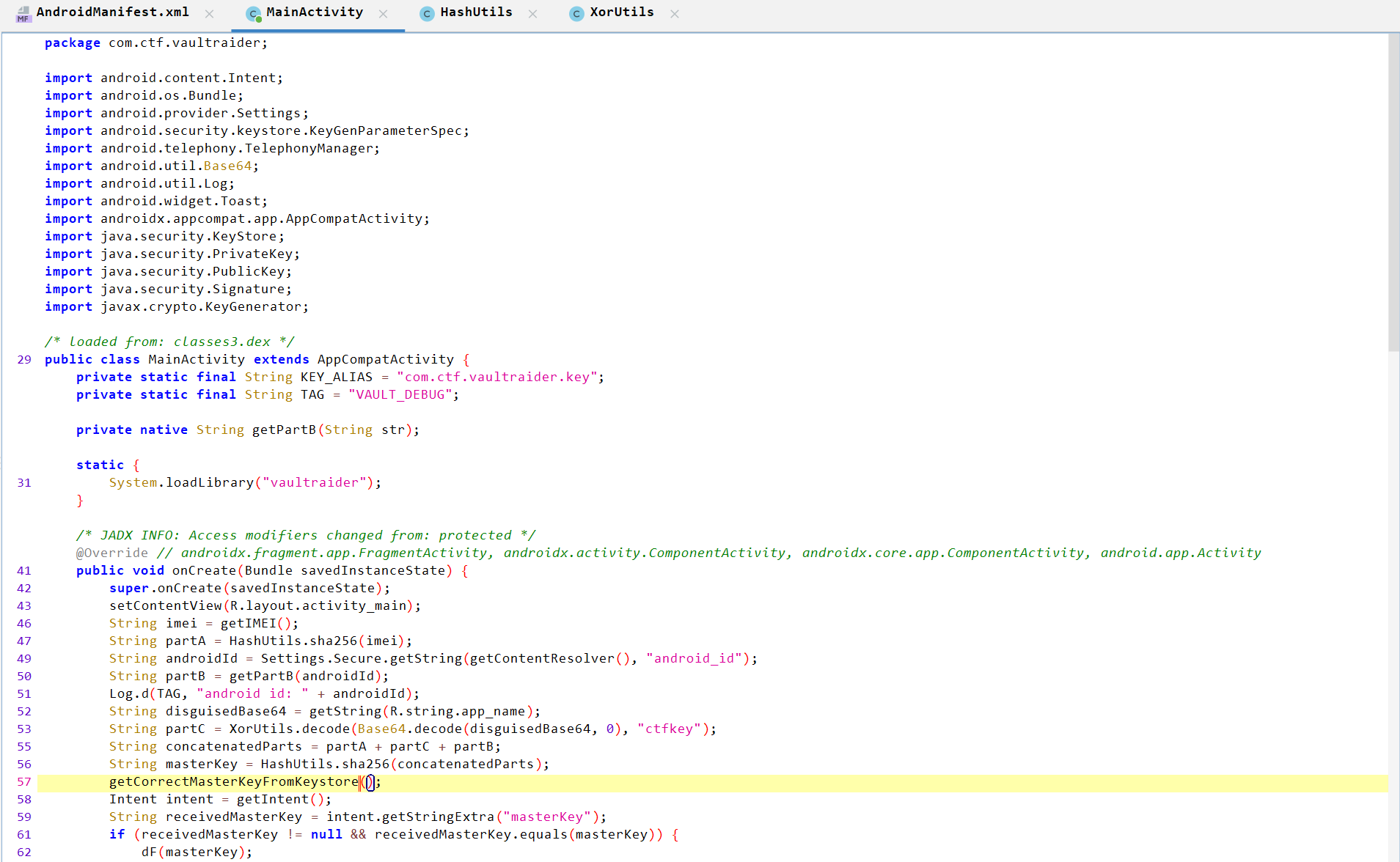
MainActivity Analysis
-
Declares
Key_ALIASEandTAGstrings with some values. -
Declares a native (JNI) method
getPartB(String str)implemented in a native librarylibvaultraider.so. -
System.loadLibrary("vaultraider")loads that library at class load time. -
onCreate()Analysis:-
Reads device
IMEI(requiresREAD_PHONE_STATEpermission). If permission missing,getIMEI()returns000000000000000.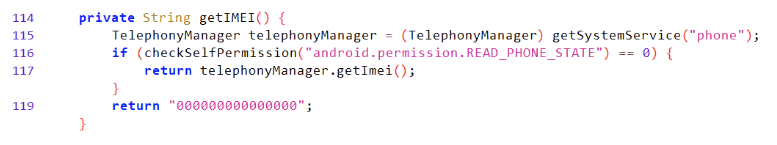
-
Passes the value of
IMEItoHashUtilsand assign its value toPartA.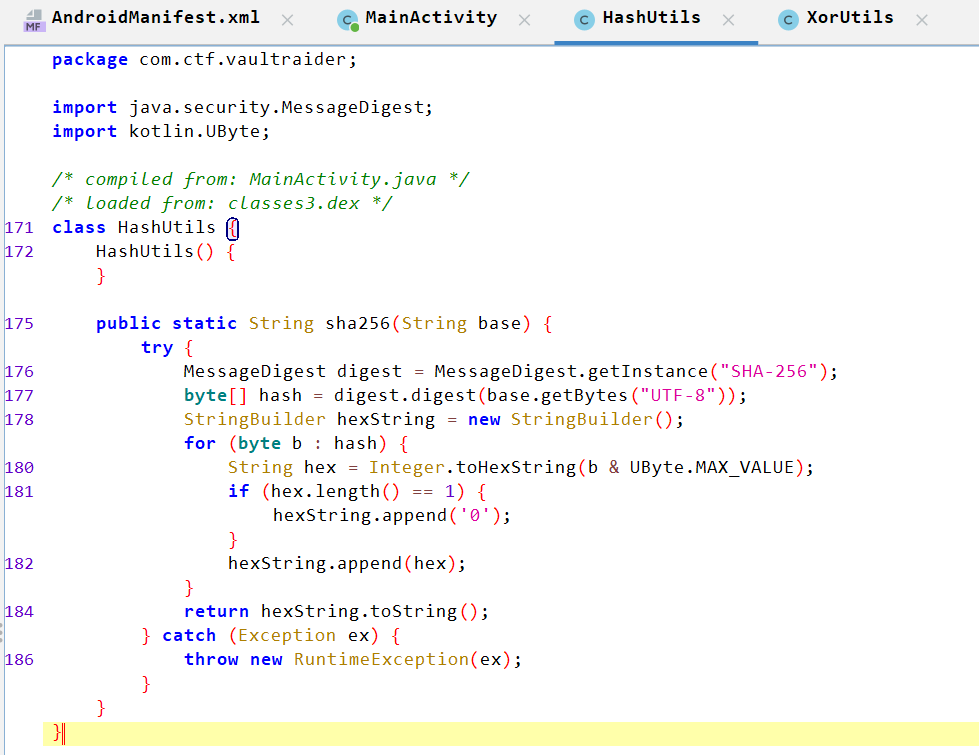
HashUtilsAnalysis:- Creates a SHA-256 digest string.
- Converts the input
Stringto bytes using UTF-8 encoding - Computes the 32-byte SHA-256 hash.
- Loop through hash and generate a SHA-256 then return SHA-256 digest lowercase hexadecimal string.
-
-
Extract device Android ID (stable per device/user) and assign it to
androidIdstring. -
Passes the value of
androidIdtogetPartBnative method and assign its value toPartB.
-
For more understanding of code, I used
ChatGPTto make it more readable.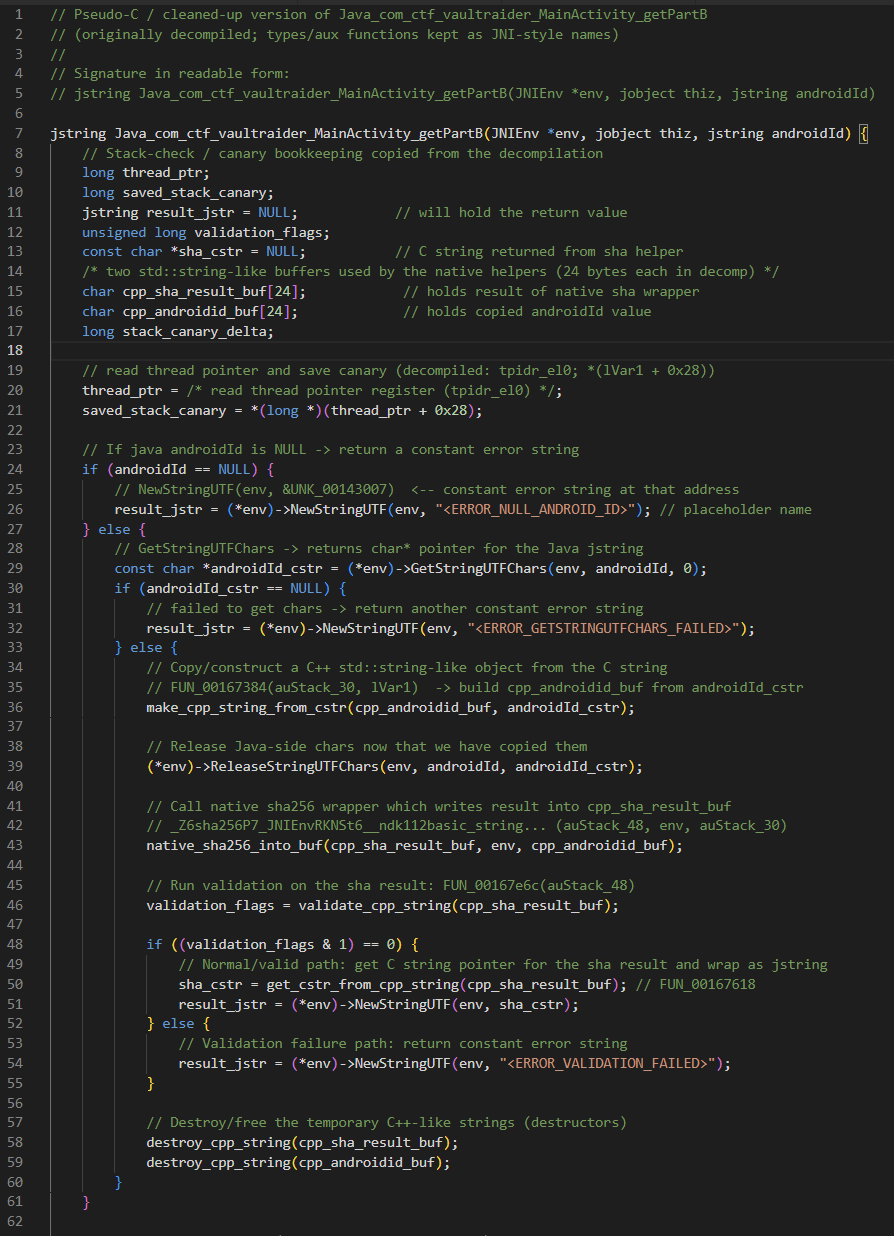
libvaultraider.soAnalysis:- The function receives the Java
androidIdstring from the Java side. - If
androidIdisnull, it immediately returns a hardcoded message (some error text). Otherwise it turns the Java string into a regular C string so the native code can read it. - It runs a small sanitization/normalization step on the string (for example: trim whitespace, remove bad characters, or force lowercase — we don’t know exact details until we inspect that sanitizer function).
- Then it computes the SHA-256 hash of that sanitized string.
- It runs a small validation check on the hash output (some internal sanity test). If the check passes, it returns the SHA-256 result (likely as a 64-character lowercase hex string). If the check fails, it returns another hardcoded error string.
- The function receives the Java
-
Gets the
app_namefromres/values/strings.xmlfile and assign its value todisguisedBase64. -
Passes the value of
androidIdtoXorUtilsmethod and assign its value toPartC.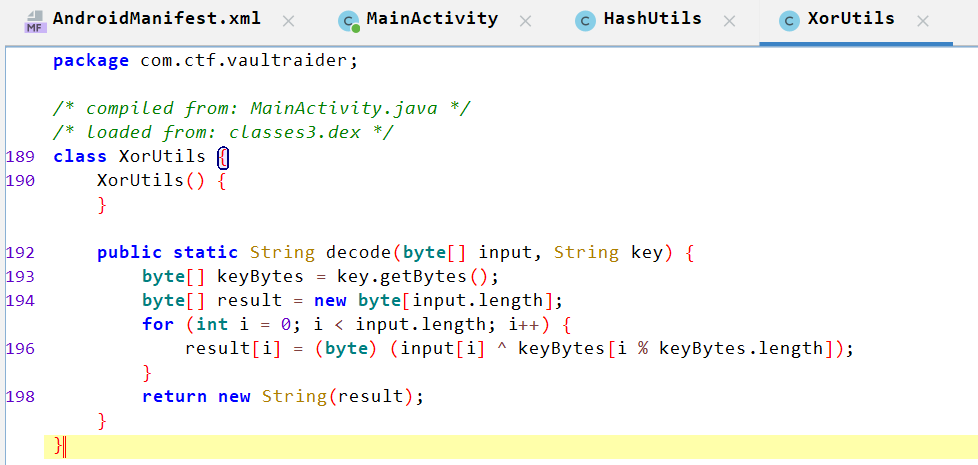
-
Concatenates
PartA + PartC + partBintoconcatenatedPartsstring. -
Passes the value of
concatenatedPartstoHashUtilsagain and assign the value tomasterKey. -
Calles
getCorrectMasterKeyFromKeystore()method.
-
App reads Intent extra
masterKey. If it matches computedmasterKey, it callsdF(masterKey), otherwise showsIncorrect master key!.
-
df()Analysis:- Builds the flag by calling
gf(mk)and wrapping result intocyctf{...}. It displays and logs the flag.
- Builds the flag by calling
-
gf()Analysis:- Takes a string
k(themasterKey) and produces a new string made of:- A fixed long hex prefix that never changes (it’s produced from a fixed list of bytes in the code),
- An underscore
_, - the first 8 characters of
kreversed, - the suffix
_solved.
- The final returned value looks like:
<prefix_hex>_<reversed-first-8-of-k>_solved
- Takes a string
-
bl()Analysis:- Does nothing relevant.
-
Let’s recap what we should do to get the flag:
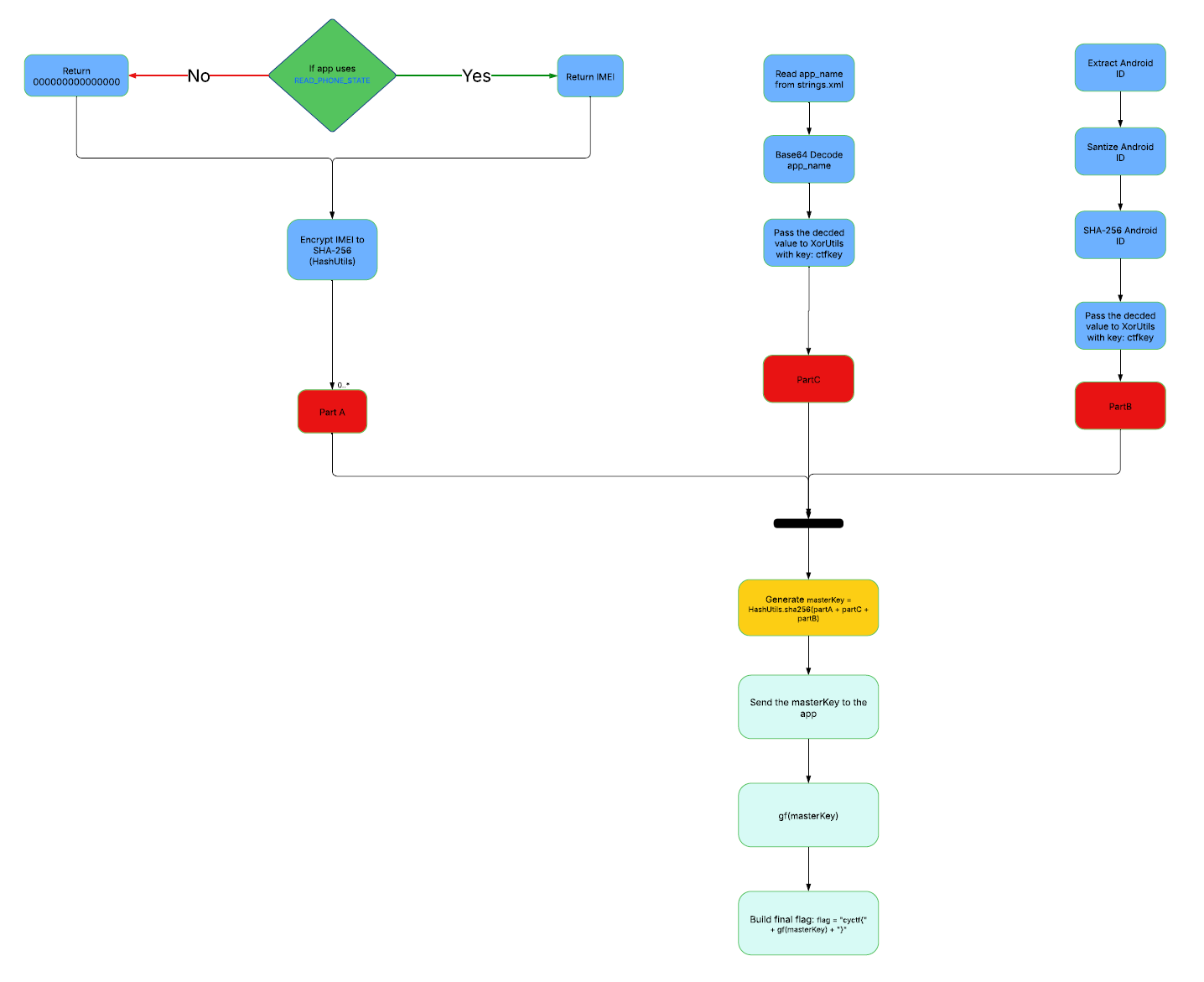
-
Get PartA:
For
PartA, actually I tried000000000000000asIMEIvalue and it worked because I use an android emulator not real device.IMEI (SHA-256):
664e7c008e22933e2358f5b74864e1c7bef2331480e6be12427457ac483fce53. -
Get Part C:
We can extract the
app_namefromres/values/strings.xml.
Let’s run the following script to get the
PartC:#!/usr/bin/env python3 import sys import argparse import base64 def xor_bytes(data: bytes, key: bytes) -> bytes: return bytes((b ^ key[i % len(key)]) for i, b in enumerate(data)) def main(): p = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Decode Base64 and XOR with repeating key") p.add_argument("b64", help="Base64 string (e.g. resource value)") p.add_argument("--key", default="ctfkey", help="XOR key (default: ctfkey)") args = p.parse_args() try: raw = base64.b64decode(args.b64, validate=True) except Exception as e: print("Base64 decode error:", e, file=sys.stderr) sys.exit(1) out = xor_bytes(raw, args.key.encode('utf-8')) # Try to decode to UTF-8 for human-readable output; fallback to hex if not valid try: text = out.decode('utf-8') except UnicodeDecodeError: text = None print("Input (base64) :", args.b64) print("Decoded bytes :", raw.hex()) print("XOR key :", args.key) if text is not None: print("Result (utf-8) :", text) else: print("Result (hex) :", out.hex()) if __name__ == "__main__": main()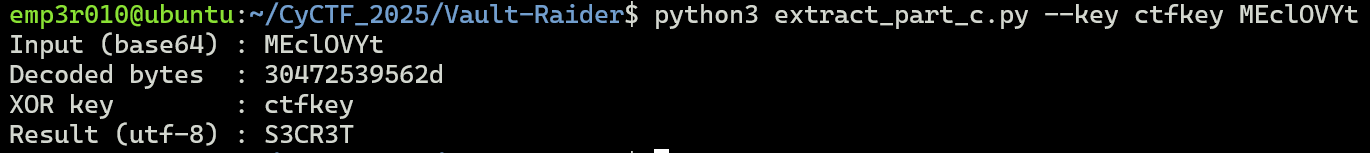
PartC:S3CR3T. -
Get Part B:
When we run the app in an android emulator, we can capture the Android ID from
logcat.
Android ID:
581582a98a0753f6.Android ID (SHA-256):
f45cc6d5ec6b7515ba791ff341b473ec0249a322fb7ac037c21bccced92bf9d5. -
Concerted String (MasterKey):
concatenated Parts = PartA + PartC + PartB 14bdcd6fd64180af5e7791df91b6af8e9a3e7bc844997eb8c29252706df97ca5S3CR3Tf45cc6d5ec6b7515ba791ff341b473ec0249a322fb7ac037c21bccced92bf9d5 -
Generate
masterKeyHash:Let’s SHA-256 encrypt the
masterKey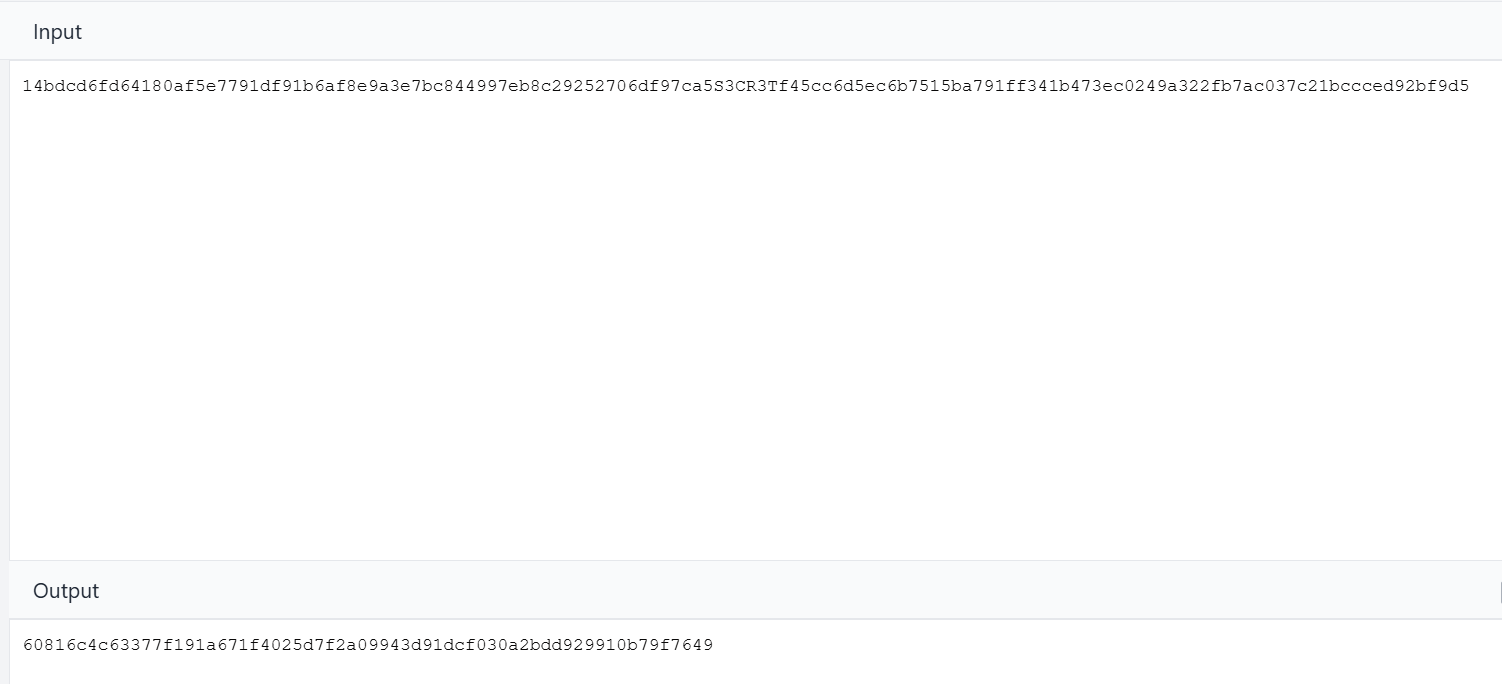
Master Key:
60816c4c63377f191a671f4025d7f2a09943d91dcf030a2bdd929910b79f7649 -
Get the flag:
Now let’s get the flag using the following script:
#!/usr/bin/env python3 # compute_flag_from_master.py # Re-implements gf(k) and dF(k) from the Java code you posted. master_key = "60816c4c63377f191a671f4025d7f2a09943d91dcf030a2bdd929910b79f7649" # z bytes from gf(); kotlin.io.encoding.Base64.padSymbol is '=' (ASCII 61) z = [52, 101, -5, 68, -98, 126, 74, -47, 99, 106, 101, 17, -96, -62, 57, 0, -66, 45, 61, -44, -84, 46, 106, 10, -43, -108, -95, -30, 59, -73, -50, -118, -100] def to_signed_byte(b): # in Java a byte is signed; formatting %02x prints two's-complement byte value return b & 0xff def compute_prefix_hex(z_bytes): return ''.join(f"{to_signed_byte(b):02x}" for b in z_bytes) def gf(k: str) -> str: prefix = compute_prefix_hex(z) # take first 8 chars of k and reverse their order first8 = k[:8] reversed_first8 = first8[::-1] return f"{prefix}_{reversed_first8}_solved" if __name__ == "__main__": gf_val = gf(master_key) flag = f"cyctf}" print("master_key:", master_key) print("gf(master_key):", gf_val) print("flag:", flag
Flag: cyctf{3465fb449e7e4ad1636a6511a0c23900be2d3dd4ac2e6a0ad594a1e23bb7ce8a9c_c4c61806_solved}